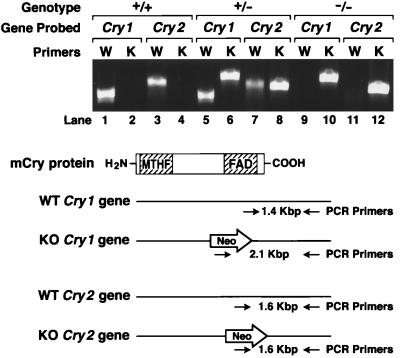
Figure 2.
Genotyping of progeny from Cry1+/−Cry2+/− cross by PCR. The knockouts of both genes each were generated by deleting a segment of the wild-type gene encoding the FAD-binding domain of CRY1 (amino acids 230–549) and of CRY2 (amino acids 349–569) and replacing it with the Neo gene. As shown in the schematic diagram, primers hybridizing to the deleted region were used to detect the wild type and primers hybridizing to the Neo gene were used to detect the mutated genes. The photograph shows results of PCR analysis of wild-type, double heterozygous, and double homozygous mutant mice.