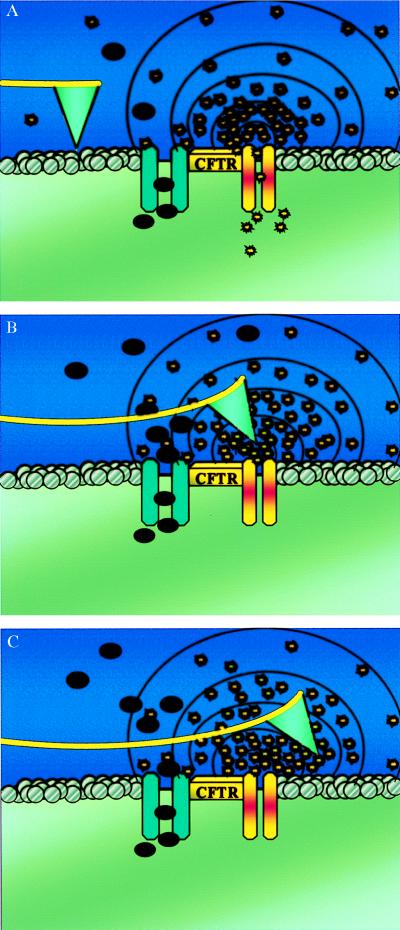
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic drawing of a functionalized S1 AFM tip imaging the extracellular surface of a CFTR expressing cell. Cl− and ATP are released in the area adjacent to the CFTR protein. The black dots represent the chloride ions, and the yellow bursts are the ATP molecules. (B) ATP molecules bind to the tip. As the enzyme hydrolyzes ATP to ADP, there is a positive deflection of the tip. The tip remains deflected as long as ATP hydrolysis continues at the tip interface. (C) After passing the point source of ATP release, the tip remains in a deflected mode because of the short contact time (20 ms) compared with the ATPase activity time (≈300 ms).