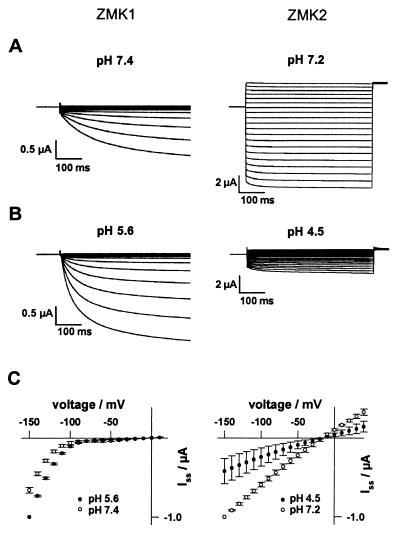
Figure 2.
Voltage dependence and pH sensitivity of ZMK1 and ZMK2 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. (A Left) Inward currents of ZMK1 were elicited in response to 500-ms voltage pulses from +10 mV to −150 mV (10-mV decrements) from a holding potential of −20 mV. (Right) From the zero current potential of ZMK2, 500-ms pulses from +40 mV to −150 mV were applied in 10-mV decrements. (B Left) Upon acidification of the extracellular solution from pH 7.4 to 5.6, ZMK1 currents increased. (Right) Upon acidification from pH 7.2 to 4.5, ZMK2 currents decreased. (C) Steady-state currents (Iss) at the end of the voltage pulses from A (○) and B (●) were normalized to Iss (−150 mV) and plotted against the membrane voltage as mean ± SE (n = 4).