Abstract
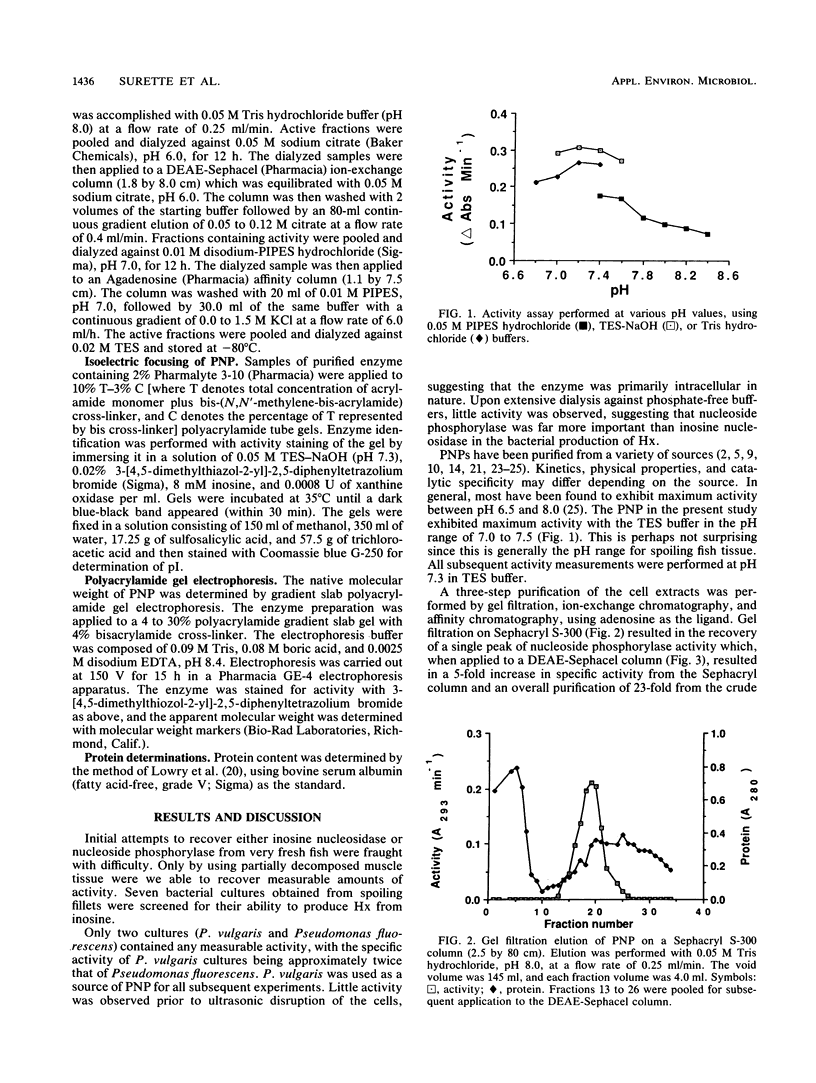
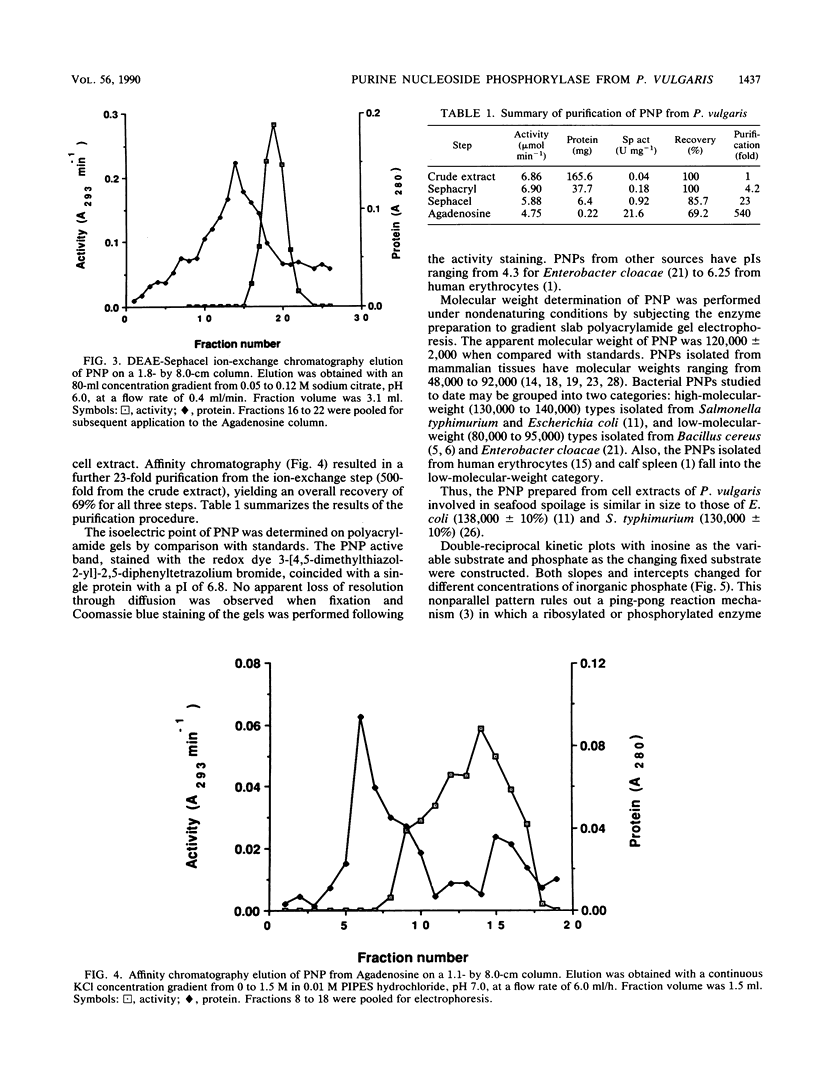
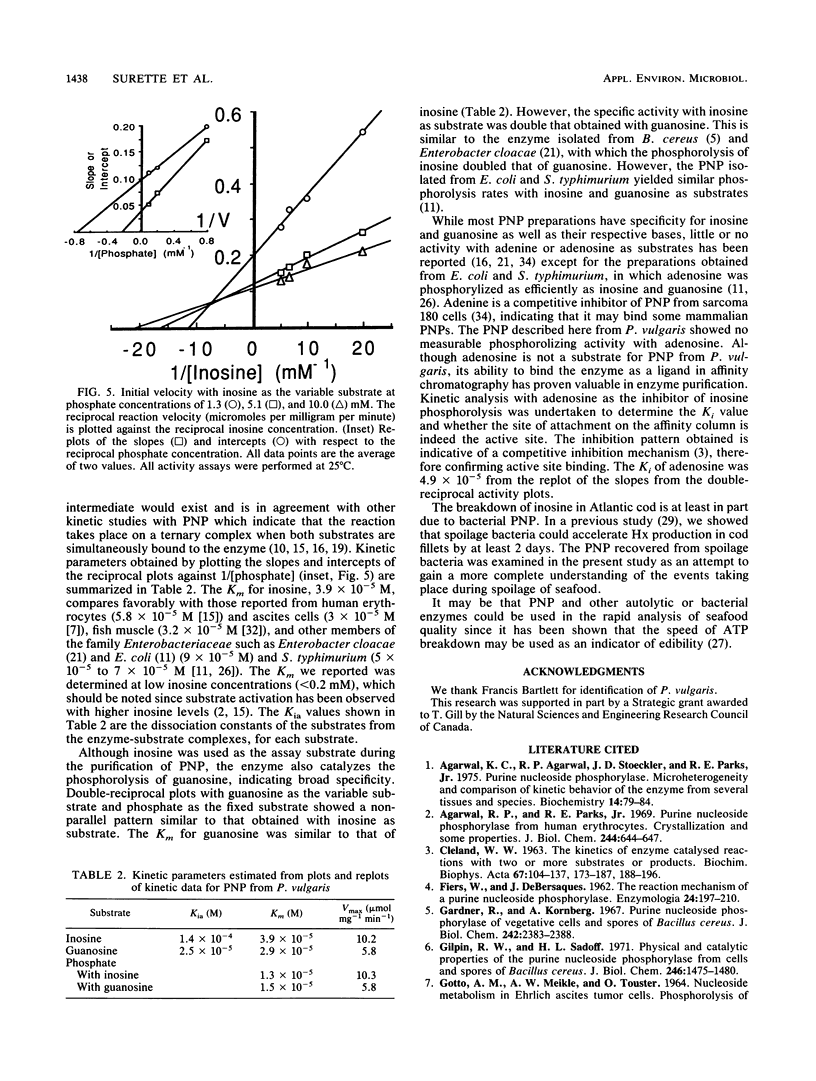
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase was isolated and purified from cell extracts of Proteus vulgaris recovered from spoiling cod fish (Gadus morhua). The molecular weight and isoelectric point of the enzyme were 120,000 +/- 2,000 and pH 6.8. The Michaelis constant for inosine as substrate was 3.9 x 10(-5). Guanosine also served as a substrate (Km = 2.9 x 10(-5). However, the enzyme was incapable of phosphorylizing adenosine. Adenosine proved to be useful as a competitive inhibitor and was used as a ligand for affinity chromatography of purine nucleoside phosphorylase following initial purification steps of gel filtration and ion-exchange chromatography.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K. C., Agarwal R. P., Stoeckler J. D., Parks R. E., Jr Purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Microheterogeneity and comparison of kinetic behavior of the enzyme from several tissues and species. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):79–84. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal R. P., Parks R. E., Jr Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from human erythrocytes. IV. Crystallization and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):644–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. II. Inhibition: nomenclature and theory. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:173–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91815-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIERS W., DE BERSAQUES J. The reaction mechanism of a nucleoside phosphorylase. Enzymologia. 1962 May 15;24:197–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTO A. M., MEIKLE A. W., TOUSTER O. NUCLEOSIDE METABOLISM IN EHRLICH ASCITES TUMOR CELLS: PHOSPHOROLYSIS OF PURINE NUCLEOSIDES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 27;80:552–561. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. V. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase of vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus cereus. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2383–2388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilpin R. W., Sadoff H. L. Physical and catalytic properties of the purine nucleoside phosphorylases from cells and spores of Bacillus cereus T. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1475–1480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada A., Igarasi S. Ribosyl and deoxyribosyl transfer by bacterial enzyme systems. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1551–1559. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1551-1559.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F., Nygaard P. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Purification and some properties. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 3;51(1):253–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K. F. Purine-nucleoside phosphorylase from Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Initial velocity kinetics, ligand banding, and reaction mechanism. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):377–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim B. K., Cha S., Parks R. E., Jr Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from human erythrocytes. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1763–1770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim B. K., Cha S., Parks R. E., Jr Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from human erythroyctes. II. Kinetic analysis and substrate-binding studies. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1771–1776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenitsky T. A. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase: kinetics, mechanism, and specificity. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 Nov;3(6):526–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. S., Glantz M. D. Bovine brain purine-nucleoside phosphorylase purification, characterization, and catalytic mechanism. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4451–4457. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. S., Glantz M. D. Monomeric purine nucleoside phosphorylase from rabbit liver. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):407–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Anton D. L., Weber J. L. Chinese hamster purine-nucleoside phosphorylase: purification, structural, and catalytic properties. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):4967–4973. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Tsushima K. Molecular properties and a nonidentical trimeric structure of purine nucleoside phosphorylase from chicken liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 26;453(1):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B. C., Hoffee P. A. Purification and properties of purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2040–2043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckler J. D., Agarwal R. P., Agarwal K. C., Schmid K., Parks R. E., Jr Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from human erythrocytes: physiocochemical properties of the crystalline enzyme. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 24;17(2):278–283. doi: 10.1021/bi00595a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARR H. L. Fish muscle riboside hydrolases. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):386–391. doi: 10.1042/bj0590386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARR H. L. Lingcod muscle purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Jun;36(6):517–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr H. L., Roy J. E. Fish-muscle purine and pyrimidine nucleoside phosphorylases. Can J Biochem. 1967 Mar;45(3):409–419. doi: 10.1139/o67-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. P., Gersten N. B., Ross A. F., Miech R. P. Adenine as substrate for purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Can J Biochem. 1971 Sep;49(9):1050–1054. doi: 10.1139/o71-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


