Abstract
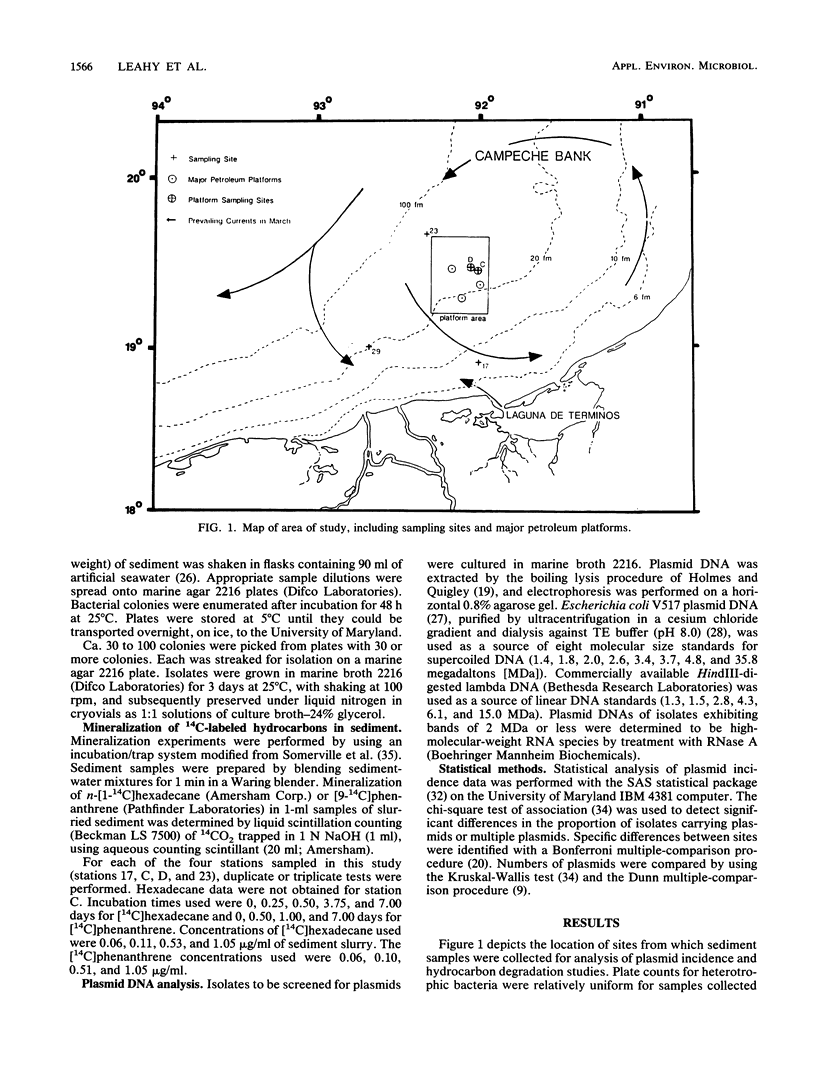
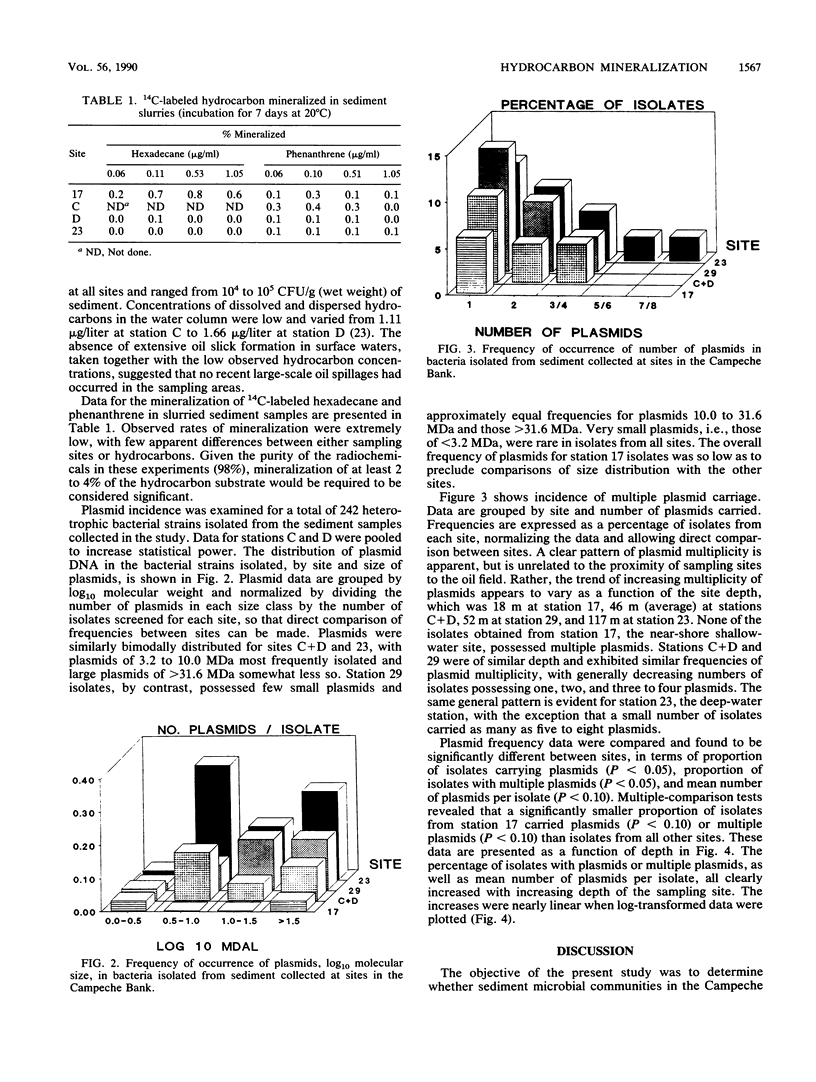
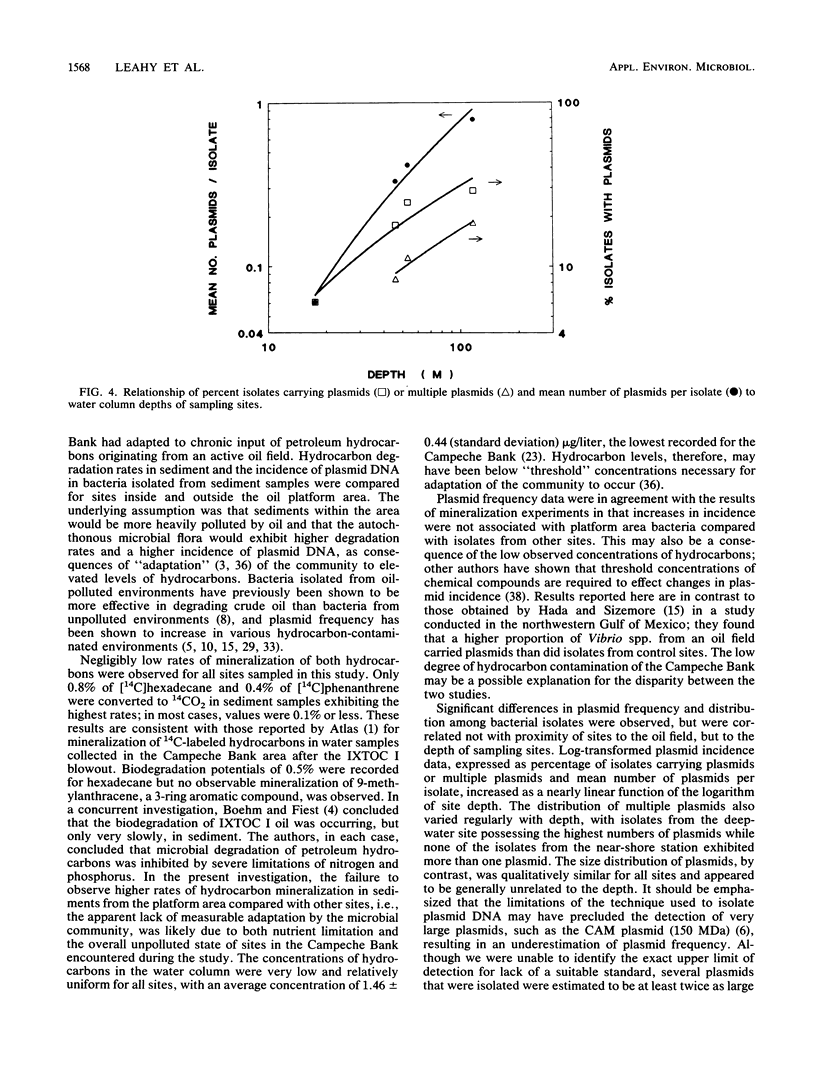
Rates of degradation of radiolabeled hydrocarbons and incidence of bacterial plasmid DNA were investigated in sediment samples collected from the Campeche Bank, Gulf of Mexico, site of an offshore oil field containing several petroleum platforms. Overall rates of mineralization of [14C]hexadecane and [14C]phenanthrene measured for sediments were negligible; <1% of the substrate was converted to CO2 in all cases. Low mineralization rates are ascribed to nutrient limitations and to lack of adaptation by microbial communities to hydrocarbon contaminants. Plasmid frequency data for sediment bacteria similarly showed no correlation with proximity to the oil field, but, instead, showed correlation with water column depth at each sampling site. Significant differences between sites were observed for proportion of isolates carrying single or multiple plasmids and mean number of plasmids per isolate, each of which increased as a function of depth.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas R. M. Microbial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: an environmental perspective. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Mar;45(1):180–209. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.1.180-209.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkay T., Pritchard H. Adaptation of aquatic microbial communities to pollutant stress. Microbiol Sci. 1988 Jun;5(6):165–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton N. F., Day M. J., Bull A. T. Distribution of bacterial plasmids in clean and polluted sites in a South Wales river. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1026–1029. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1026-1029.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmids in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R. Ecological aspects of microbial degradation of petroleum in the marine environment. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977 Sep;5(4):423–445. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson J. K., Hicks R. J., Li S. W., Brockman F. J. Plasmid incidence in bacteria from deep subsurface sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2916–2923. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2916-2923.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hada H. S., Sizemore R. K. Incidence of Plasmids in Marine Vibrio spp. Isolated from an Oil Field in the Northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):199–202. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.199-202.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansson M., Jones G. W., Kjelleberg S. Frequency of antibiotic and heavy metal resistance, pigmentation, and plasmids in bacteria of the marine air-water interface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2338–2342. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2338-2342.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobori H., Sullivan C. W., Shizuya H. Bacterial plasmids in antarctic natural microbial assemblages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):515–518. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.515-518.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville C. C., Monti C. A., Spain J. C. Modification of the 14C most-probable-number method for use with nonpolar and volatile substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):711–713. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.711-713.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Pritchard P. H., Bourquin A. W. Effects of adaptation on biodegradation rates in sediment/water cores from estuarine and freshwater environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):726–734. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.726-734.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickham G. S., Atlas R. M. Plasmid frequency fluctuations in bacterial populations from chemically stressed soil communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Sep;54(9):2192–2196. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.9.2192-2196.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


