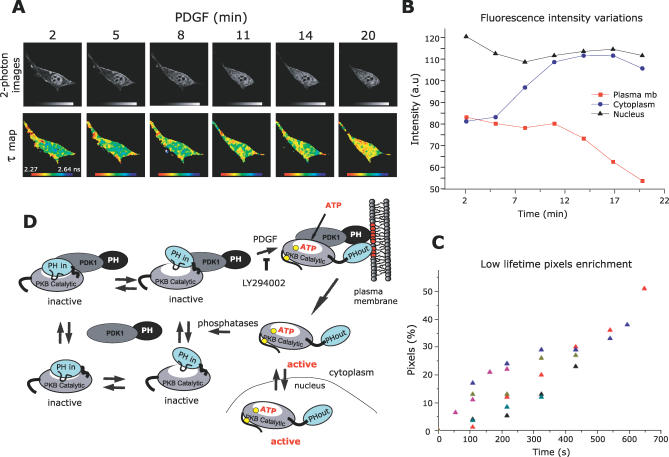
Figure 4. PKB Conformation Dynamics Revealed in Live Cells.
(A) A series of two-photon FLIM images of a GFP-PKB-RFP–transfected NIH3T3 cell were acquired over a period of 20 min (every 54 s). The top panels represent intensity images of the donor GFP chromophore in the transfected cell after two photon excitation. The bottom panels represent the calculated lifetime maps of GFP-PKB-RFP over time. After treatment with 60 ng/ml PDGF, cells were observed under the microscope. Acquisition took place once the construct had translocated to the membrane. The lifetimes are represented in pseudo-colour scale ranging from 2.27 to 2.64 ns.
(B) The variations of fluorescence intensity at the plasma membrane (red squares) in the cytoplasm (blue circles) and in the nucleus (black triangles) were detected over time.
(C) The time-course graph presents the enrichment in short lifetime pixels of six different experiments. Each coloured triangle presents a cell. The enrichment of short lifetime pixels is calculated as described in Supporting Information.
(D) Under basal conditions, PKB and PDK1 form a complex in the cytoplasm where the associated and dissociated forms are in dynamic equilibrium. Four possible equilibrium states of PKB–PDK1 complex in its inactive conformation are represented. In the PKB inactive conformation, PKB PH and kinase domains interact, noted as “PH-in.” The equilibrium between a “tighter” and a “looser” interaction of PKB PH with its kinase domain is also represented. Upon PDGF stimulation, the PKB–PDK1 complex is recruited to the plasma membrane due to interaction with phosphoinositides (in red). The equilibrium of PKB–PDK1 interaction is shifted toward the associated form, a process compromised by LY294002. The interaction of PKB PH domain with the lipids induces a change in conformation of PKB, noted as “PH-out.” In this conformation, Thr308 becomes accessible to PDK1 (the phosphorylation sites are represented by yellow circles). After Ser473 phosphorylation and loading of ATP, PKB dissociates from the plasma membrane in its active conformation to return to the cytoplasm and the nucleus. PKB re-adopts an inactive conformation upon dephosphorylation of its Thr308 and Ser473 sites.