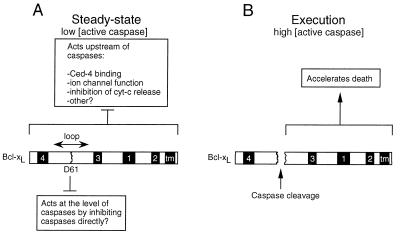
Figure 5.
A model for regulation of cell death by Bcl-xL. (A) Under normal conditions (low concentrations of active caspases), Bcl-xL may have two separate anti-death functions, one that acts through factors binding to the BH1 domain and acts upstream of caspases (7–13, 26) and the other, localized in the loop domain, that functions to directly inhibit low levels of active caspases. (B) When the death stimulus has overwhelmed the anti-death activity of Bcl-xL, higher levels of active caspases accumulate, and cleavage of the loop region of Bcl-xL leads to the accumulation of Bcl-xL cleavage product that may accelerate the death process. Numbered boxes refer to the BH domains in Bcl-xL, and tm indicates the transmembrane domain.