Fig. 3.
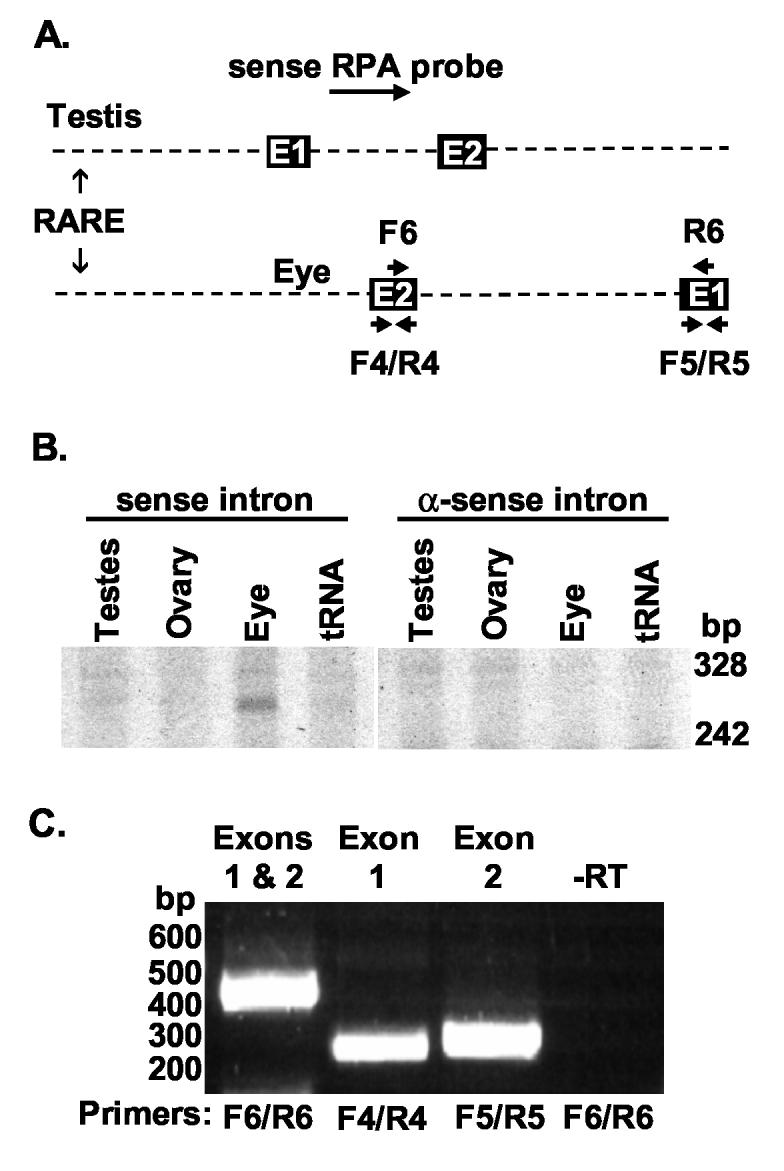
The C13 RARE is downstream of an RNA expressed in neonatal eye. A. A diagram showing the relative locations of the RPA probe and RT-PCR primers used in B and C. E1 and E2 refer to exons 1 and 2 of each transcript. B. RPAs using probes derived from the intron of the testes RNA were performed on RNAs from day 10 eyes and mature testes and ovary. These RNAs overlapped the last 261 nt. of the eye transcript. Sense probes relative to the testis transcript, but not anti-sense probes, protected an ∼261 nt. RNA in eye, but not ovary or testis, RNA. C. An RT-PCR using the primer pairs shown in the diagram amplified the products predicted by the alignment of the ESTs to the genome. Primers spanning the intron between exon 1 (E1) and 2 (E2) (F6 and R6) yielded the expected fragment of 415 nt., but not the greater than two kb fragment that would have been generated from genomic DNA or unspliced RNA. Primers F4 and R4 in exon 2 of the eye transcript yielded the expected fragments of 260 nt. Primers F5 and R5 in exon 1 of the eye transcript yielded the expected fragments of 271 nt. This reaction is representative of several reactions. No amplification ever occurred in reactions containing RNA but lacking reverse transcriptase (-RT) or in those lacking RNA (not shown).
