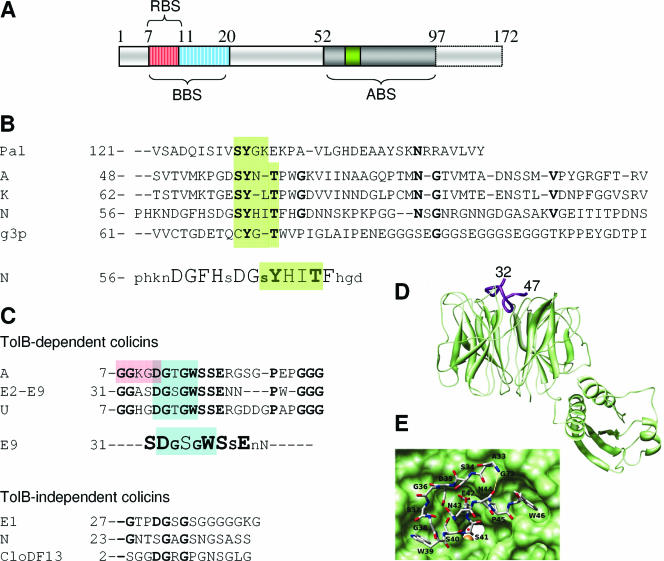
FIG. 8.
Tol binding sequences. (A) Schematic illustration of the colicin A N-terminal domain and the three binding sequences identified (RBS, TolR-binding sequence, residues 7 to 11; BBS, TolB-binding sequence, residues 7 to 20; ABS, TolA-binding sequence, residues 52 to 97) (42, 43, 313). (B) Sequence alignments of the Pal, colicins A, K, and N, and g3p TolA binding sequences. Conserved residues are in boldface type, and the TolA binding motif with the conserved and critical tyrosine residue is highlighted in green (78, 527). Lower panel, results from alanine-scanning mutagenesis of residues 56 to 75 of colicin N (228). Uppercase letters, essential residues; lowercase letters, nonessential residues. (C) Sequence alignments of the TolB-dependent (upper panel) and -independent (lower panel) colicin TolB binding sequences. Conserved residues are in boldface type. Colicin TolB boxes are highlighted in blue, whereas the colicin A TolR binding sequence is framed. Note that the WSSE motif present in TolB-dependent colicin TolB binding sequences is not found in TolB-independent colicins. Middle panel, results from alanine-scanning mutagenesis of residues 34 to 44 of colicin E9 (248). Large letters, critical residues; small letters, nonessential residues; medium letters, mutations decreasing but not abolishing TolB-colicin E9 N-terminal domain affinity. (D) Crystal structure of the TolB protein (green) with the residues 32 to 47 of colicin E9 (purple) (417) showing localization of the TolB binding sequence at the entrance of the β-propeller. (E) Top view of the same complex, which emphasizes the binding site. The colicin E9 peptide is represented in a backbone. (Panels D and E are reprinted from reference 417 with permission of the publisher. Copyright 2006 National Academy of Sciences U.S.A.)