Fig. 4. Impaired mTEC development in NF-κB2−/− mice.
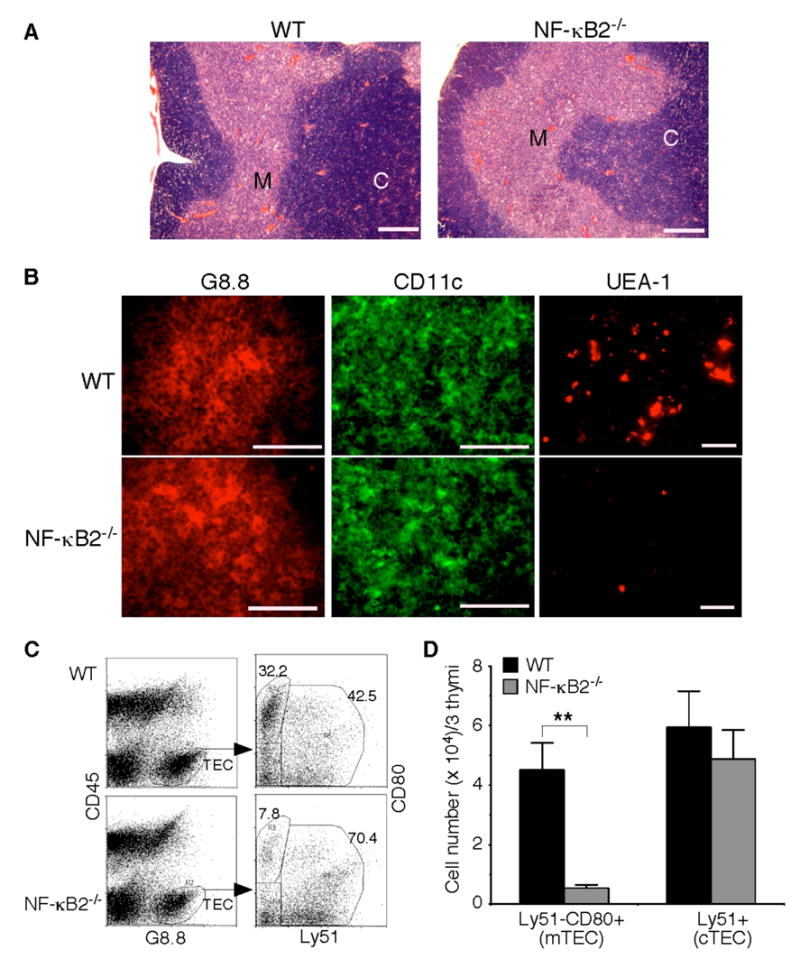
A, H&E staining of formalin-fixed thymic sections of 4- to 6-week-old NF-κB2−/− and wild-type mice. Shown is representative staining of thymic sections from 5 mice for each genotype. Scale bars, 500 μm. M, medulla; C, cortex. B, Immunofluorescence staining of thymic sections of 4- to 6-week-old NF-κB2−/− and wild-type mice for G8.8 (an epithelial cell marker), CD11c (a DC marker), or UEA-1 (a marker for mature mTECs). Shown is representative staining of thymic sections from 5 mice for each genotype. Scale bars, 100 μm. C–D, Flow cytometry analysis of thymic epithelial cell populations. Pooled thymic stromal cells from 3 NF-κB2−/− or wild-type mice of 4 to 6 weeks of age were stained with antibodies to CD45, G8.8, CD80, and Ly51. Mature mTECs are CD45−G8.8+Ly51−CD80+, and cTECs are CD45−G8.8+Ly51+. Data in D represent means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments with total 9 mice for each genotype. ** Student’s t-test, p<0.01.
