Figure 1.
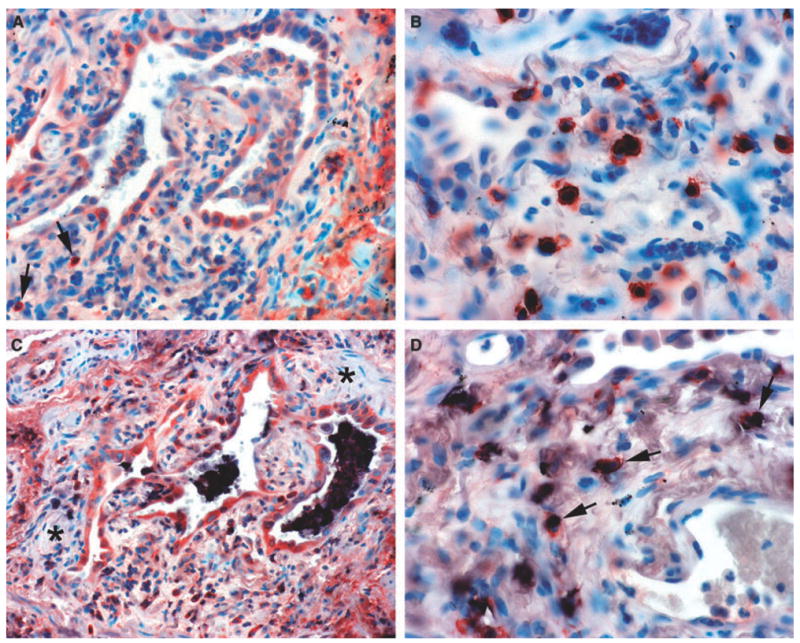
Extracellular superoxide dismutase (ECSOD) immunoreactivity in usual interstitial pneumonia and double labelling for mast cells and alveolar macrophages. A, Variable expression of ECSOD in type 2 pneumocytes, alveolar macrophages and a few interstitial cells (arrows). B, Strong expression of ECSOD in granular interstitial cells evidently representing mast cells. C, Alveolar macrophages showing staining for both CD68 (indicated by black) and ECSOD (same cells also showing red). Notice that type 2 pneumocytes and a few interstitial cells at the bottom are positive for ECSOD (red). Notice also that the fibroblast foci (asterisks) are negative for ECSOD. D, Mast cells showing staining for both ECSOD (red ) and CD117 (black) (arrows).
