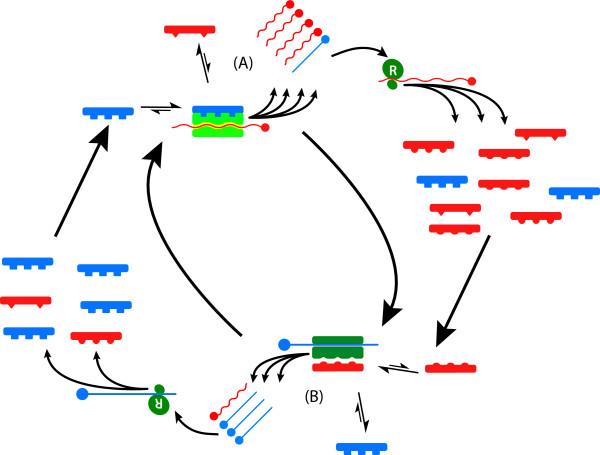
Figure 3.
Mechanism of replicative homeostasis. (A) High concentrations of consensus sequence Envwt (blue, A) favour high affinity Envwt:RNApol interactions that out-compete variant forms (Envmt, red), and alter RNApol conformation that increase RNApol processivity and reduce fidelity, thus increasing the relative output of variant RNAs (red). Subsequent ribosomal (R, green) translation increases concentration of Envmt (red), relative to Envwt, reverting the system to equilibrium. Relative excess of Envmt (B, red) out-compete Envwt (blue) for interactions with RNApol, favouring Envmt:RNApol, and blocking Envwt:RNApol interactions again altering RNApol conformation, the Envmt:RNApol complexes decrease RNApol processivity and increase fidelity, increasing output of wild-type RNAs. Subsequent increased translation of Envwt relative to Envmt restores the equilibrium.