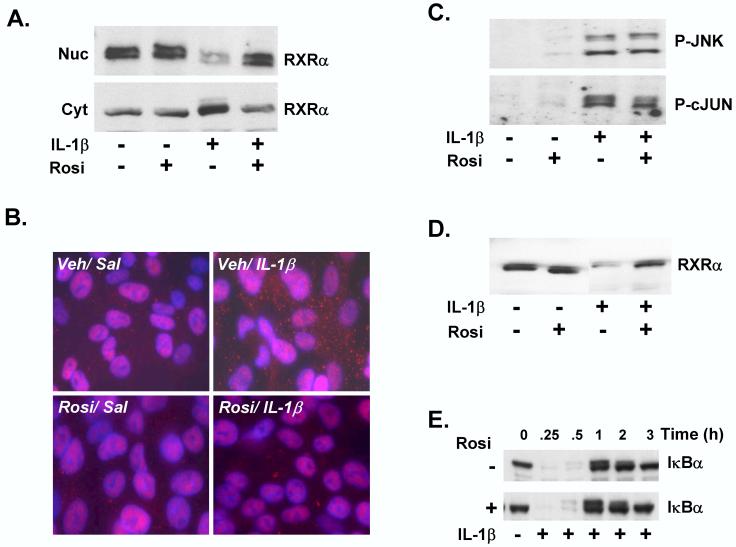
Figure 4.
Rosiglitazone attenuates IL-1β -mediated RXRα nuclear export and degradation in vitro. HepG2 cells were pre-treated for 30 mins. with 10 μM Rosi or DMSO vehicle, followed by treatment with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) or vehicle control (0.0001% BSA in PBS) for 30 minutes. (A) Nuclear (Nuc) and cytosolic (Cyt) extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to RXRα to determine the effects of Rosi on subcellular localization of RXRα in the presence of IL-1β. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of saline or IL-1β-treated HepG2 cells, pre-treated with vehicle or Rosi. The cells were stained with Alexa-Fluor-labeled antibody detecting RXRα, DAPI-staining of the nuclei, and the merged images are shown. (C) Nuclear protein levels of P-JNK (upper panel) or P-c-JUN were determined at 30 and 60 mins. of IL-1β treatment, preceeded by pre-incubation with Rosi. (D) Whole cell extracts (WCEs) were probed with RXRα antibodies to determine the effect of Rosi on protein levels of RXRα in total cell extracts, after IL-1β treatment. (E) Total cell lysates were prepared from HepG2 cells treated with DMSO or Rosi, prior to treatment with IL-1β from 0 - 3 hours. The samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with IκBα antibodies.