Figure 7. p300 (HAT) is preferentially associated with RNA Polymerase II in the coding regions of SV40 chromosomes undergoing transcription.
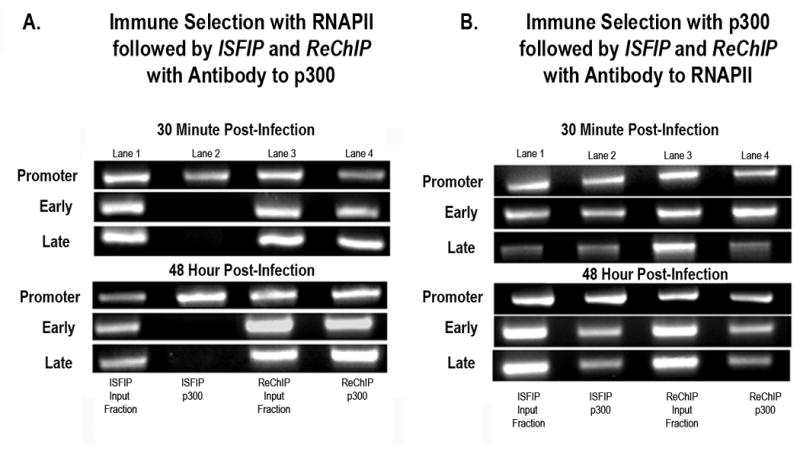
A: Unfixed SV40 chromosomes were isolated from cells infected with 776 wild type virus for 30 minutes or 48 hours and subjected to an ISFIP/ReChIP analysis with antibody to p300 as described in the materials and methods. The samples were amplified by simplex PCR with primer sets to the early, late and promoter regions. The position of the amplification product from the wild-type 776 DNA is indicated. Lane 1: ISFIP input fraction; lane 2: ChIP with 10 μl of p300 antibody (ISFIP); lane 3: ReChIP input fraction; lane 4: ChIP with 10 μl of p300 antibody (ReChIP); B: Unfixed SV40 chromosomes were isolated from cells infected with 776 wild type virus for 30 minutes or 48 hours and subjected to an ISFIP/ReChIP analysis with antibody to RNAPII as described in the materials and methods. The samples were amplified by simplex PCR with primer sets to the early, late and promoter regions. The position of the amplification product from the wild-type 776 DNA is indicated. Lane 1: ISFIP input fraction; lane 2: ChIP with 10 μl of RNAPII antibody (ISFIP); lane 3: ReChIP input fraction; lane 4: ChIP with 10 μl of RNAPII antibody (ReChIP). The PCR products in the ISFIP and ReChIP lanes were amplified from one half of the total amount of DNA obtained from each of the samples. The PCR products in the input lanes were amplified from one fourth of the total amount of DNA present in each of the input samples. Similar results were obtained from at least three separate preparations of SV40 chromosomes for each time point
