Figure 2.
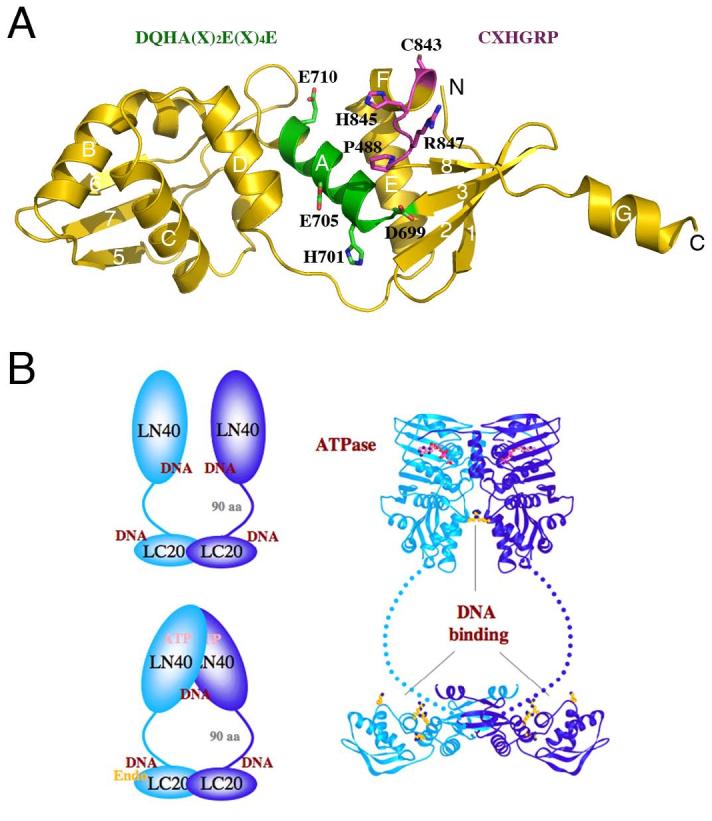
Structural model of MutLα. A. A model of the C-terminal domain of PMS2 based on the E. coli MutL structure [8] (PDB accession: 1X9Z). The DQHA(X)2E(X)4E and CXHGRP motifs are highlighted in the ribbon diagram and written out above the diagram in the same color. B. The overall structure of an MutL dimer. The C-terminal domains of MutL form a stable dimer in E. coli and humans. The N-terminal ATPase domains associate in the presence of ATP and dissociate in its absence. The linker between the two domains contains ∼100-300 residues and adopts a rather extended conformation in E. coli MutL. Both the N- and C-terminal domains of E. coli and yeast MutL have been shown to interact with DNA. The DNA-binding region in the C-terminal domain of E. coli MutL coincides with the divalent cation-binding site in PMS2. Since MLH1 has no metal ion-binding site, MutLα is predicted to contain a single endonuclease active site. Homodimeric bacterial MutL proteins may have two endonuclease active sites per molecule, but the endonuclease activity may be asymmetric upon association with MutS and a mismatch site.
