Figure 2.
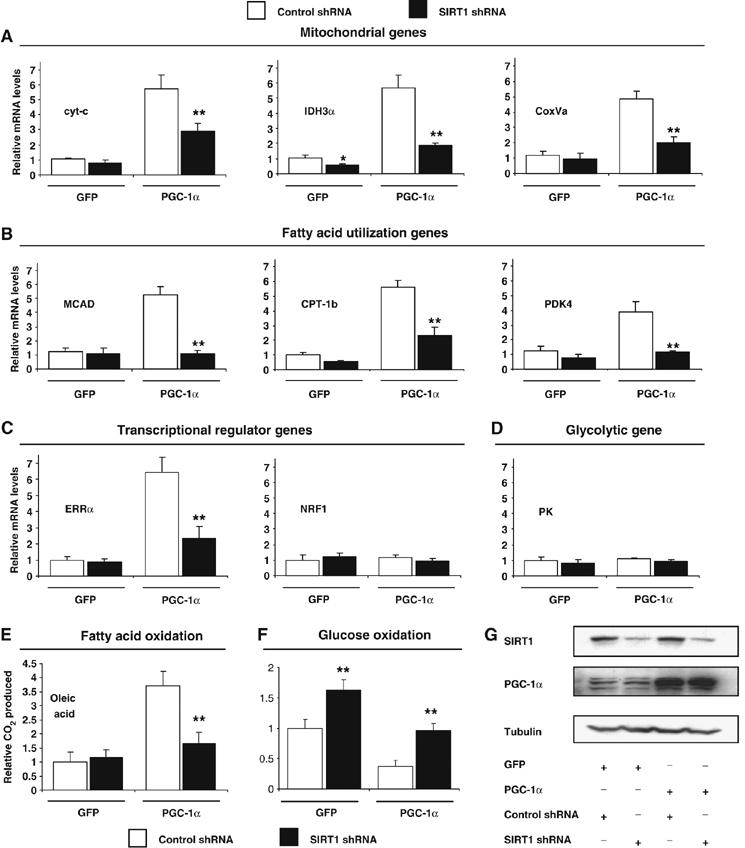
SIRT1 regulates PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial and fatty acid metabolism in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. (A) SIRT1 knockdown decreases PGC-1α-induced mitochondrial, (B) fatty acid utilization, (C) ERRα, but not (D) pyruvate kinase gene expression. C2C12 myotubes were infected for 3 days with the indicated adenoviruses. After harvesting, RNA was extracted and used for measuring indicated gene expression using quantitative RT–PCR analysis. (E) PGC-1α-induced oxidation rates of fatty acids are reduced by SIRT1 knockdown. C2C12 myotubes were treated as in (A). Oleic acid oxidation rates were measured as described in Materials and methods. (F) PGC-1α-decreased oxidation rates of glucose are prevented by SIRT1 knockdown. Glucose oxidation rates were measured in C2C12 myotubes as described in Materials and methods. (G) Knockdown of SIRT1 in C2C12 myotubes. Cells were infected with the different adenoviruses as in (A–F). Protein cell extracts were used for Western blot analysis that was performed with the indicated antibodies. Values represent the mean of 2–3 experiments performed in duplicate. Error bars represent s.e.m. Statistical analyses were performed using Student's t-test. *P<0.05 and **P<0.005, shRNA control versus shRNA SIRT1.
