Figure 9.
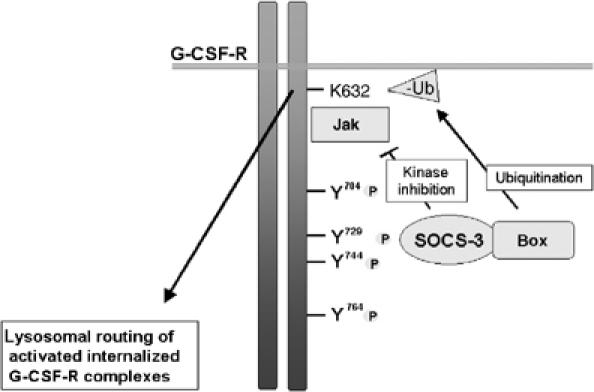
Model of SOCS3-controlled termination of G-CSF signaling. Following activation by G-CSF, G-CSFR recruits SOCS3 via phosphorylated tyrosine residue Y729. SOCS3 inhibits JAK activity via its kinase inhibitory region to inactivation of G-CSFR. This may also be achieved in part by direct recruitment of SOCS3 to JAK itself (Kile and Alexander, 2001). A second and novel mechanism involves recruitment of E3 ligase activity, leading to ubiquitination of K632 of G-CSFR. This triggers G-CSFR transition from Hrs-positive endosomes to lysosomes, attenuating activation of STAT5.
