Figure 4.
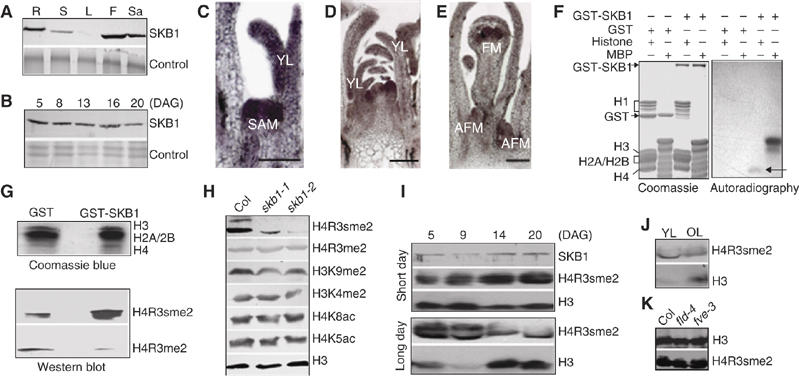
Analysis of SKB1 expression pattern and methyltransferase activity. (A, B) Immunoblot analyses of SKB1 with the use of polyclonal anti-SKB1 antiserum. (A) Total protein extracts from different tissues of the wild type at 38 days. R, root; S, stem; L, leaf; F, flower; Sa, silique. Control shows equal loading. (B) Expression of SKB1 protein at different developmental stages. Col was grown under LD and whole parts were harvested at the indicated growth stages for total protein isolation. (C–E) RNA in situ hybridization analysis of SKB1 expression in Col grown under LD for 10 (C), 21 (D) and 26 (E) days. AFM: axillary flower meristem; SAM, shoot apical meristem; FM, floral meristem; YL, young leaf. Scale bar, 100 μm. (F) In vitro methylation of histones (10 μg) and myelin basic protein (MBP, 10 μg) by GST-SKB1 (2 μg) purified from E. coli. GST (3 μg) was a negative control; left, Coomassie blue-stained gel; right, autoradiograph of 3H-labelled proteins produced by in vitro methylation; methylated H4 is indicated by an arrow. (G) SKB1-mediated H4R3sme2 was analyzed by Western blot with specific antibodies. (H) Western blot analysis of modification of histone H3 and H4. Histone-enriched protein extracts from 20-day-old Col and skb1 mutant plants grown under LD were probed with antibodies that specifically recognize the indicated forms of histone H3 and H4. (I) Levels of SKB1 and H4R3sme2 at different developmental stages in Col. Total soluble proteins isolated from seedlings grown in SD were exposed to antibody against SKB1. Histone-enriched proteins were extracted from plants grown under SD or LD and immunoblotted with antibodies against H4R3sme2 and H3. (J) The level of H4R3sme2 in specific tissues of Col grown under LD. YL: young leaves plus apex from seedlings at 5 DAG; OL: old leaves from plants at 35 DAG. (K) Abundance of H4R3sme2 in Col, fld-4 and fve-3. Proteins were isolated from seedlings grown at 20 DAG under LD.
