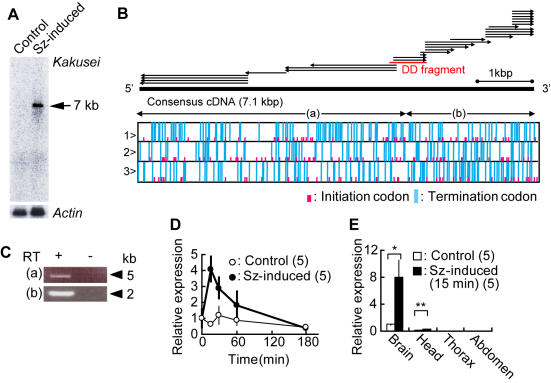
Figure 1.
Identification and characterization of a novel non-coding immediate early gene, kakusei. (A) Northern blot analysis was performed using RNAs extracted from the brains of workers collected 15 min after seizure induction (Sz-induced lane) and workers anesthetized with CO2 for 15 min (Control lane). Using the same membrane, actin was detected as a loading control. The approximately 7-kb long signal is indicated by a triangle. (B) Overview of kakusei cDNA contig and open reading frame analysis. Arrows indicate cDNA subclones identified by 5′-and 3′-rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) methods. The thin red bar in the middle of the arrows shows the DNA fragment identified by differential display screening (DD fragment). The solid bar indicates the full-length consensus kakusei cDNA. Lower box indicates open reading frame analysis in each reading frame of the consensus kakusei DNA. Note the lack of significantly long open reading frames. (C) Actual expression of the assembled cDNA sequence was confirmed by RT-PCR using primers designed to amplify the regions shown in (B). Bands of the expected size were detected for both regions (a) and (b), and the sequence was the same as the consensus sequence. Experiments were repeated five times, and performed with (+) or without (−) the RT (reverse transcriptase) reaction, confirming that there is no genomic DNA contamination in the samples. (D) Time course of kakusei expression investigated by real-time RT-PCR. (E) Kakusei expression in various body parts investigated by real-time RT-PCR (*, P = 0.0487; **, P = 0.0036; Student's t-test). All data are shown as the means±SEM.