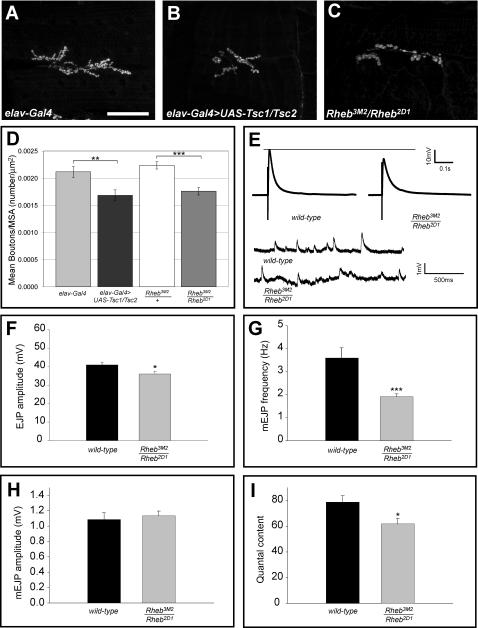
Figure 2. Rheb activity is required for normal synapse assembly.
Panels A–C show anti-CSP staining of larval NMJs in a control animal (A, elav-Gal4 driver alone), an animal bearing elav-Gal4>UAS-Tsc1, UAS-Tsc2 (B), or a Rheb partial loss of function mutant (C). Reduction of Rheb function produced by either neuron-directed expression of Tsc1 and Tsc2 (n = 22) or mutation of Rheb (n = 40) significantly reduced synapse size compared to controls with elav-Gal4 alone (n = 44) or animals heterozygous for a Rheb mutation (n = 17), as measured by the number of synaptic boutons/muscle area (D). Panel E shows sample EJP traces for wild-type and Rheb mutant NMJs, as well as baseline recordings from these preparations showing the size and frequency of mini-EJPs. Panels F, G, and I show reductions in EJP amplitude, mini-EJP frequency, and quantal content for Rheb mutant synapses (n = 29) compared to wild-type controls (n = 10). Mini-EJP amplitude did not show a significant change (H). The scale bar in A is 50 microns.