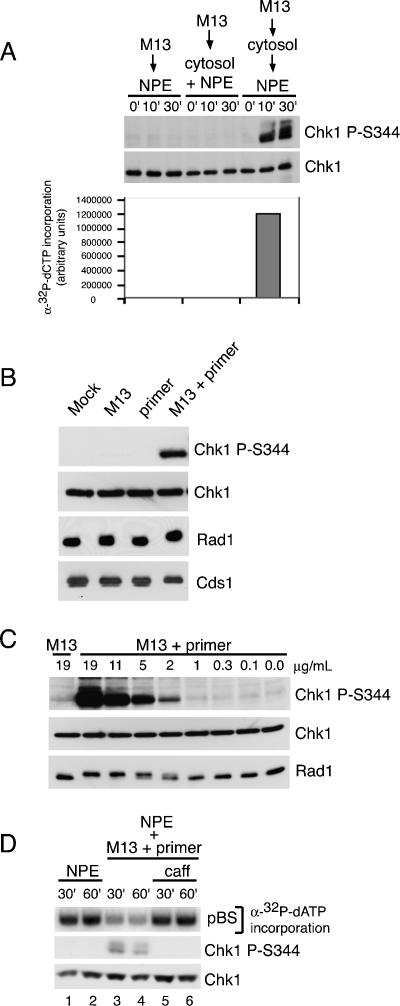
Figure 1.
Primed M13 ssDNA induces Chk1 phosphorylation and checkpoint activation. (A) M13 ssDNA (30 μg/mL) was added to NPE, a 1:1 mixture of cytosol and NPE, or cytosol (30 min) and then NPE. Parallel samples were removed at the indicated times post-DNA addition for NPE and cytosol + NPE. For the sequential addition, times were post-NPE addition. Samples were either immunoblotted for phospho-Chk1 (S344) and Chk1 (top panels), or replication was monitored by measuring α32P-dCTP incorporation following gel electrophoresis (bottom). (B) Buffer, M13 ssDNA, the ssDNA primer (80-mer), or M13 preannealed to the primer (M13 + primer) was added to NPE. Samples were taken after 20 min and analyzed by immunoblotting after SDS-PAGE with antibodies for phospho-Chk1 (S344), Chk1, Rad1, and Cds1. (C) ssM13 DNA or M13 + primer was added to NPE at the indicated concentrations. Samples were analyzed as in B. (D) Double-stranded pBS (30 μg/mL) was incubated in cytosol for 30 min and added to an equal volume of NPE (lanes 1,2), NPE containing M13 + primer (20 min; 12.5 μg/mL; lanes 3,4), or NPE containing M13 + primer + caffeine (20 min; 12.5 μg/mL; caff, 4 mM; lanes 5,6). Parallel samples were removed 30 and 60 min post-addition of plasmid to NPE and analyzed for replication as in A (top panel) or immunoblotted for phospho-Chk1 (S344) and Chk1 (bottom panels). Final concentrations are shown.