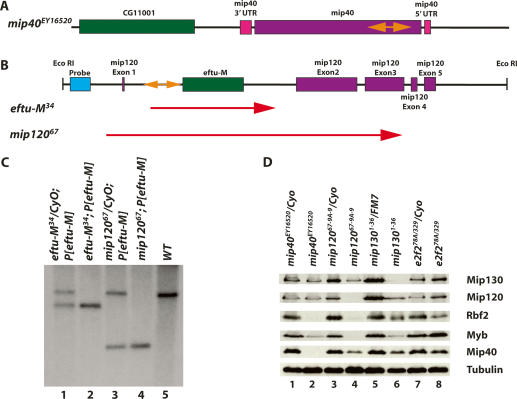
Figure 1.
Molecular verification of the mip40 and mip120 mutants. (A) The chromosomal configuration of the mip40 locus is shown (purple and pink), along with the location of the P-element insert in the mip40-coding sequence (orange double-sided arrow). (B) The chromosomal configuration of the mip120 locus is shown, with the mip120 exons in pink. The location of eftu-M (CG6050) within the first mip120 intron is shown in green. The P-element insertion for line KG05422 is shown in orange. The location of the probe used in C (blue) and the EcoRI restriction sites are also shown. The two lines generated after mobilization of the P-element and used in this study, eftu-M34 and mip12067, are shown. The regions deleted in these mutants are indicated by the red arrows. (C) Southern blot of eftu-M34 and mip12067 containing a transgene expressing eftu-M on the third chromosome (P[eftu-M]). Shown are EcoRI digests of DNA isolated from the strains indicated on the top and probed with the DNA fragment shown in B. The size of the deletion in each mutant as determined by sequence analysis is as follows: eftu-M34, 2236 bp; mip12067, 5770 bp. (D) Whole animals of the indicated genotypes were homogenized in sample buffer. “e2f2” refers to flies derived from crossing e2f2329/CyoKrGFP and e2f278A/CyoKrGFP (Cayirlioglu et al. 2001). Fly equivalents (0.3) were loaded onto a 9% SDS-PAGE, immunoblotted, and analyzed for the accumulation of the indicated MMB subunit using affinity-purified antibodies. Tubulin served as the loading control.