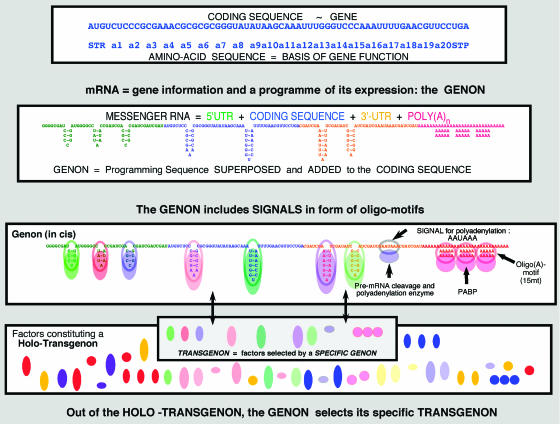
Figure 2.
Coding sequence, gene, genon and transgenon: the amino-acid sequence of a polypeptide represents the gene, as the basis of a function; its equivalent at RNA level is the coding sequence which is inserted into the mRNA and framed by the 5′-end and 3′-end UTRs. In the latter and superimposed onto the coding sequence is the genon, a programme in cis of sequence oligomotifs, eventual binding sites for regulatory proteins (or si/miRNAs—not shown). The holo-Transgenon of a given cell is constituted by all these factors, which eventually will recognise the oligomotifs (empty coloured circles) in the genon in cis. A subset of factors (filled circles) interacting with a specific mRNA constitute the latter's Transgenon (PABP: poly(A)-binding protein). If the gene is a functional RNA, the same formalism applies.