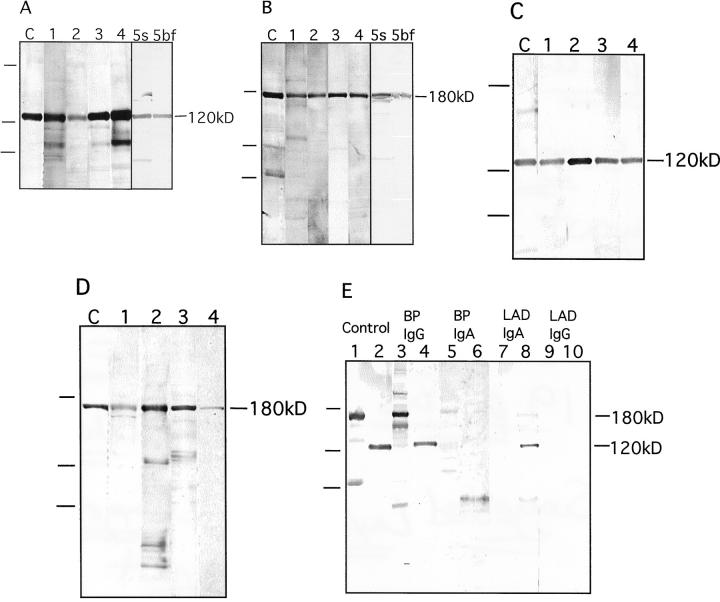
Figure 5.
IgG and IgA autoantibody reactivity with two forms of collagen XVII. A: IgG reactivity with the 120-kd soluble ectodomain of collagen XVII. Lane C: Control antibody Ecto1. Lanes 1–4 show reactivity with four different bullous pemphigoid sera. Serum (lane 5s) and blister fluid (lane 5bf) of yet another bullous pemphigoid patient contained similar amounts of autoantibodies. B: IgG reactivity with 180-kd full-length collagen XVII. Lane C: Control antibody Ecto1. Lanes 1–4 show reactivity with four different bullous pemphigoid sera. Autoantibodies in serum (lane 5s) or in blister fluid (lane 5bf) of yet another bullous pemphigoid patient contained similar amounts of autoantibodies. C: IgA reactivity with the 120-kd soluble ectodomain of collagen XVII. Lane C: Control antibody Ecto1. Lane 1: A CBDC serum. Lanes 2–4: Three different LAD sera. D: IgA reactivity with 180-kd full-length collagen XVII. Lane C: Control antibody Ecto1. Lane 1: A CBDC serum. Lanes 2–4: Three different LAD sera (not the same sera as in C). On the left of the panels, migration positions of molecular weight mass are indicated. From top to bottom: 200, 112, and 80 kd. E: Specificity of the IgG or IgA autoantibody response in the patient serum was tested using chain-specific secondary antibodies, and full-length collagen XVII (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9) and the soluble ectodomain (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) as antigens. The following antibodies were used: control antibody Ecto1 (lanes 1 and 2), bullous pemphigoid serum with anti-human IgG second antibodies (lanes 3 and 4), and anti-human IgA second antibodies (lanes 5 and 6); LAD serum with anti-human IgA second antibodies (lanes 7 and 8) and anti-human IgG second antibodies (lanes 9 and 10). The tests showed that the pemphigoid sera contained practically no IgA reactivity and the LAD sera no IgG reactivity. On the left, migration positions of molecular weight mass are indicated. From top to bottom: 200, 112, and 80 kd.