Figure 9.
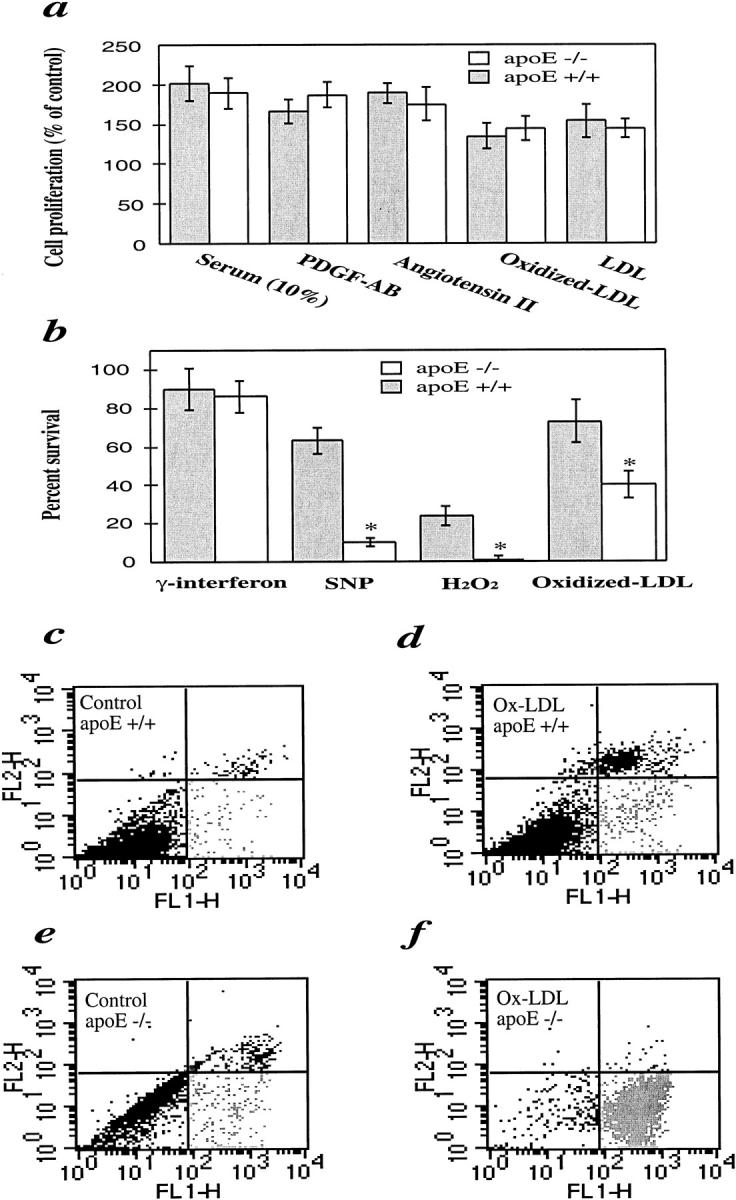
Comparison of SMC proliferation (a), viability (b), and apoptosis/necrosis (c-f) between apoE−/− and apoE+/+ mice. a: Serum-starved SMCs were treated with platelet-derived growth factor-AB (50 ng/ml), angiotensin II (50 nmol/L), fetal calf serum (10%), LDL (100 μg/ml), and oxidized LDL (10 μg/ml), respectively, at 37°C for 24 hours. b: SMCs were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours with oxidized LDL (200 μg/ml), H2O2 (50 μmol/L), sodium nitroprusside (SNP; 0.5 mmol/L), and γ-interferon (100 ng/ml). Solution of proliferation/apoptosis kit was added 4 hours before measurement. The optical density at 490 nm was recorded with a photometry. Data are means ± SD of three experiments. *Significant difference between apoE−/− and apoE+/+ SMCs. c–f: FACS analysis of annexin V/propidium iodide double-stained SMCs. SMCs were treated with oxidized LDL (d and f) for 24 hours and labeled with annexin V and propidium iodide. Cellular fluorescence signal was recorded on FL1 and FL2 channels of a FACS scan flow cytometer and expressed on a logarithmic scale. Note the higher number of spontaneous cell death (c and e) and oxidized LDL-induced apoptosis (d and f) in apoE−/− SMCs.
