Figure 1.
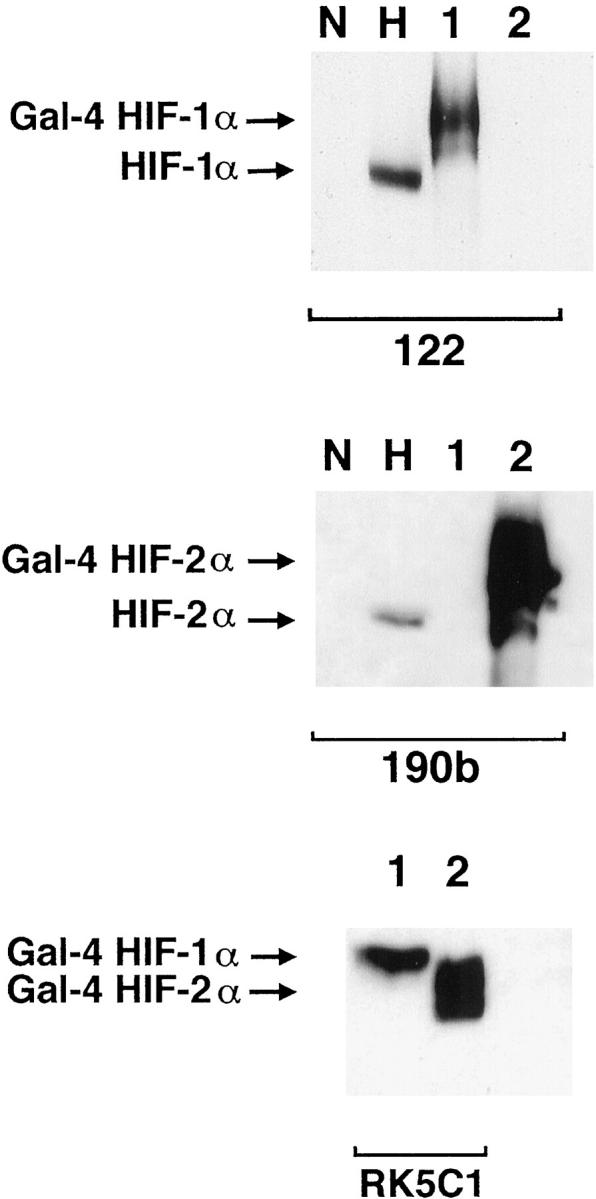
Western blots showing specificity of mAbs used for immunostaining. Whole cell extracts were prepared from HeLa cells cultured in parallel for 4 hours in normoxia (N) and 0.1% hypoxia (H) and COS-1 cells transfected with either pGN/HIF-1α28–826 (lane 1) or pGN/HIF-2α19–870 (lane 2). Transfection resulted in the expression of fusion proteins between the N-terminal Gal4 DNA binding domain and the indicated amino acids of the respective HIF α chains. Preliminary analysis (not shown) using the Gal4 mAb established the amount of each COS extract required to give approximately equal Gal4 signal, indicating similar amounts of HIF-1α and HIF-2α fusion proteins. These were loaded with 50 μg of HeLa extracts and separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membrane and analyzed in parallel using mAb 122 (HIF-1α), 190b (HIF-2α), and RK5C1 (Gal4) as primary antibodies. mAb 122 detects a single band in extracts from COS cells transfected with pGN/HIF-1α28–826 and no bands in extracts from COS cells transfected with pGN/HIF-2α19–870, whereas the opposite pattern is seen with mAb 190b. Detection of comigrating bands with an antibody to the GAL4 DNA binding domain (RK5C1) confirms the identity of these bands as the respective fusion proteins. The antibodies to HIF-1α and HIF-2α recognize hypoxically inducible proteins of 135 kd and 110 kd, respectively, in the HeLa cell extracts, compatible with the known migration of endogenous HIF-1α and HIF-2α on SDS-PAGE.
