Figure 8.
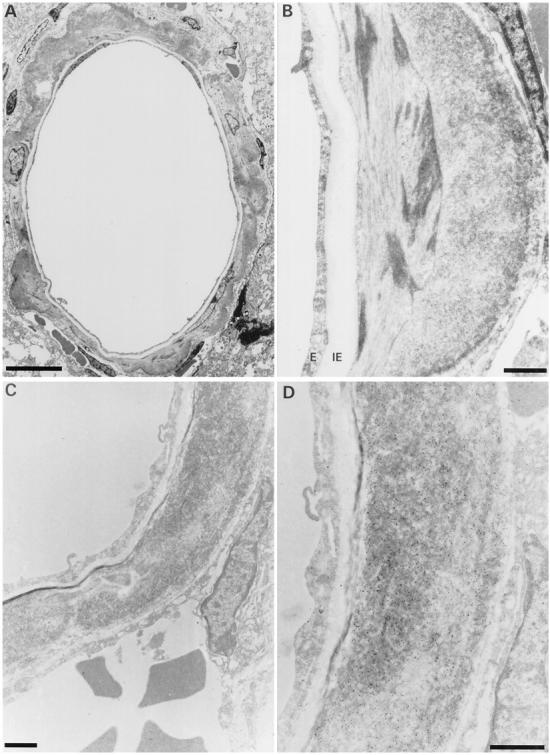
Ultrastructural aspect of dilated cerebral blood vessel from an unperfused FVB/N APP/Ld mouse. A: Dilated vessel with circumferential amyloid deposition. The endothelial layer is thinned and the internal elastic lamina is stretched. B: Higher magnification of amyloid deposit. The amyloid deposit is situated in the outermost part of the smooth muscle layer. E, endothelium; IE, internal elastic lamina. C: Serial section of same blood vessel stained for Aβ40. The smooth muscle layer is replaced by a large mass of amyloid fibers. D: High magnification showing the gold particles on the amyloid fibers. The endothelium and the internal elastic lamina are intact, whereas the smooth muscle layer and the external elastic lamina are disrupted. Scale bars, 10 μm (A) and 1 μm (B–D).
