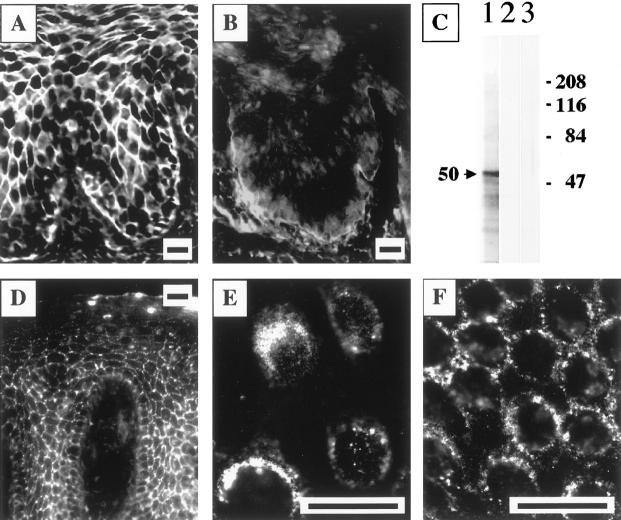
Figure 2.
Visualization of keratinocyte α9 AChR—a novel PV antigen. A and B: Specific blocking of the immunostaining of the cell membranes of keratinocytes by FITC-conjugated rabbit anti-α9 monoepitopic antibody because of preincubation with the PV serum PRC-45. The strong intercellular staining of the cryostat section of monkey esophagus resulting from anti-α9 antibody binding to the cell membrane (A) was completely eliminated in the specimen preincubated with PV (B) but not normal human serum (not shown). Scale bars, 50 μm. C: Characterization of the affinity-purified monoepitopic anti-α9 AChR rabbit antibody. The sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis-resolved membrane protein extract of cultured human oral keratinocytes was used as the substrate for immunoblotting. The anti-α9 antibody recognized a protein that migrated with an apparent molecular weight of 50 kd (lane 1). The specificity of this single-band antibody binding was illustrated by the ability to abolish the staining in control experiments, in which a strip of the immunoblotting membrane was exposed to the anti-α9 antibody that had been preincubated overnight with 150 nmol of the peptide immunogens (lane 2). In another set of control experiments, no staining was detected when the primary antibody was omitted (lane 3). The molecular weight markers in kd are shown on the right. D–F: Visualization of α9 AChR on the keratinocyte cell membrane. In a series of indirect immunofluorescence experiments, nonpermeabilized specimens of normal human attached gingiva (D) and a second passage preconfluent (E) or confluent (F) monolayers of normal human gingival keratinocytes were incubated with immunoaffinity-purified rabbit anti-α9 AChR antibody, and its binding was visualized by using secondary, FITC-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG antibody, as detailed in the Material and Methods. The antibody visualized α9 AChR on the cell membrane of keratinocytes, producing a characteristic intercellular, or pemphigus-like fishnet staining of the epithelium (D). In keratinocyte monolayers, the antibody decorated the cell surface of preconfluent cultured keratinocytes (E), and was found clustered at the sites of cell-to-cell contacts in confluent cultures (F), indicating that α9 AChRs are localized predominantly to the areas of keratinocyte cell membrane associated with cell-to-cell contacts. Scale bars, 50 μm.