Figure 3. Pain intensity has a large effect on brain activity for rating spontaneous pain of PHN, and for rating the visual control task.
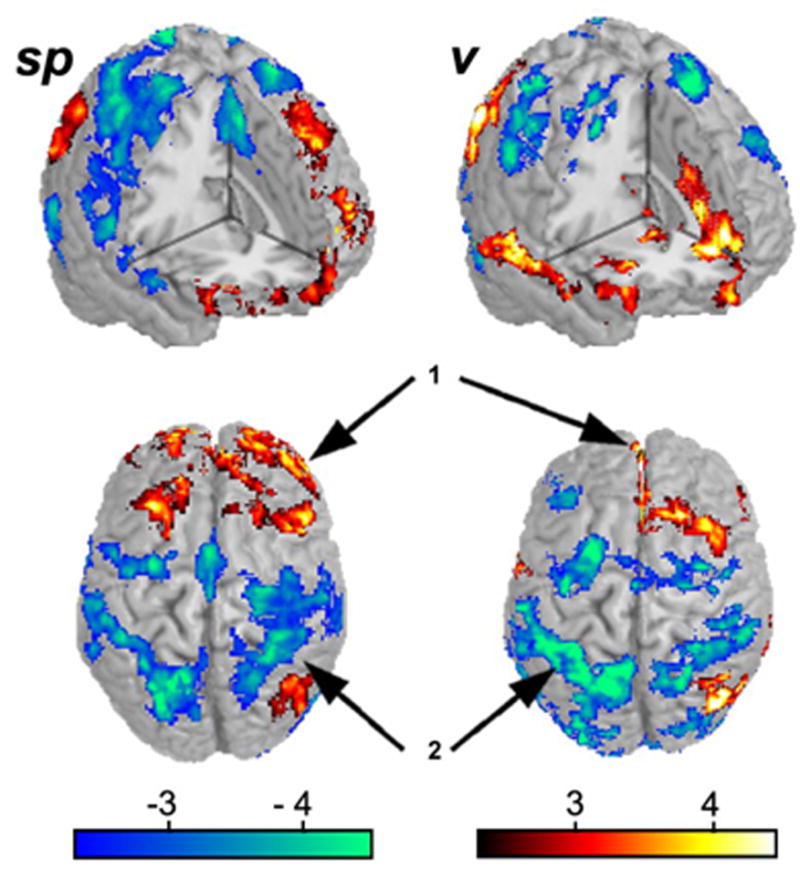
Brain activity for rating spontaneous pain (sp) or rating visual control (v) task were correlated with the average pain rating at the time of the scan. Generally, in both tasks similar regions were modulated with average spontaneous PHN pain: medial and lateral prefrontal areas were positively modulated (arrow 1), while posterior parietal attentional areas (arrow 2) were negatively modulated..
