Figure 1.
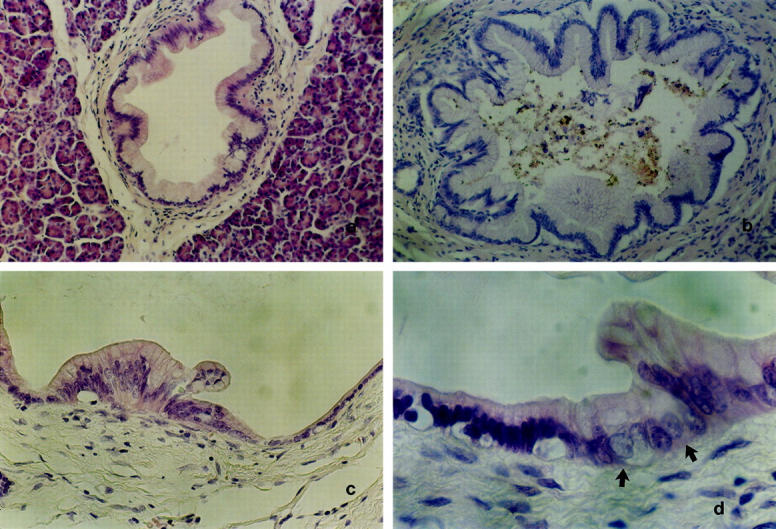
Representative examples of microdissected PILs. a: PIL 1. Mostly flat epithelial lesion composed of uniformly tall columnar mucin-filled cells with mostly basally located nuclei which do not show signs of atypia (H&E; original magnification, ×250). b: PIL 2. Epithelial lesion consisted of mucin-filled cells with basally located nuclei without signs of atypia and a papillary growth pattern, some papillary folds typically showing a fibrovascular stalk (H&E; original magnification, ×250). c: PIL 3. Epithelial lesion exhibiting mucinous epithelium with nuclear crowding and focal loss of nuclear polarity resembling moderate dysplasia falling short of PIL 4 (H&E; original magnification, ×400). d: PIL 4. Epithelial lesion (arrows) showing cytological criteria of severe nuclear abnormalities like prominent nucleoli, hyperchromasia, loss of polarity, irregular size, and contours (H&E; original magnification, ×650).
