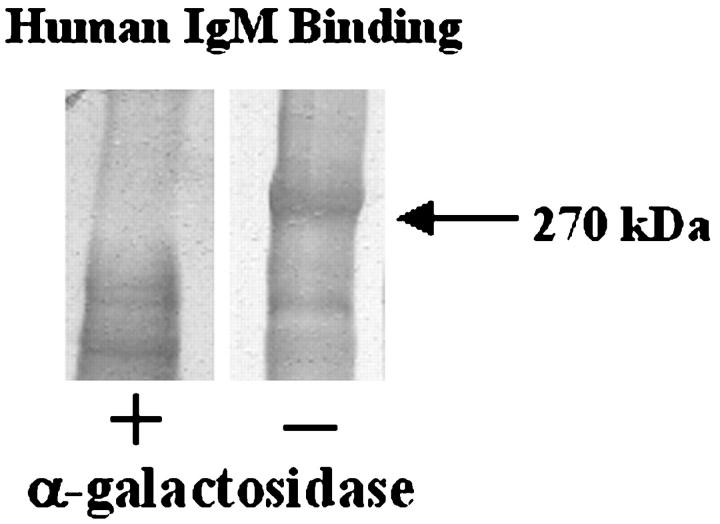
Figure 7.
Presence of Galα1-3Gal in immune complexes in the blood of baboons, after pulmonary xenotransplantation. Immune complexes in the serum taken from baboon blood after a pulmonary xenotransplantation were diluted 5:1 with 12% PEG 8000 and 60 mmol/L EDTA in VBS for 16 hours at 4°C to precipitate immune complexes. The solution was centrifuged at 2,000 × g for 20 minutes at 4°C to pellet immune complexes. Precipitates were resuspended in digestion buffer (100 mmol/L NaCl and 50 mmol/L sodium acetate). Samples were incubated with (+) or without (−) α-galactosidase (1 U/ml) for 5 hours at 37°C. Proteins were precipitated with ethanol, reduced, separated by SDS-PAGE (7.5% PA), and transferred to PVDF. The blots were reacted with human serum as a source of xenoreactive IgM and then with anti-human IgM. Lane 1, α-galactosidase digested proteins targeted by human IgM, Lane 2, control proteins targeted by human IgM. Digestion of samples with α-galactosidase abrogates the binding of human xenoreactive IgM.