Figure 1.
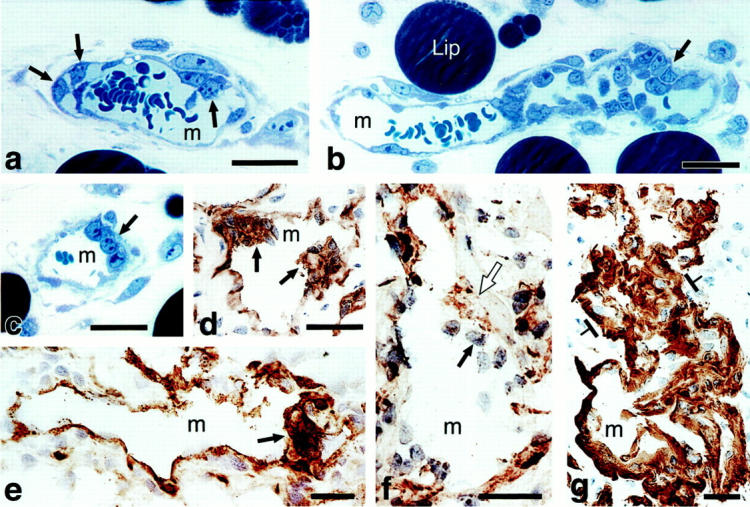
Primitive GBs developing in mother vessels 3 to 4 days after injection of adeno-vpf/vegf into ears of athymic mice. a–c: One-micron-thick, Giemsa-stained Epon sections illustrating focal accumulations of large, primitive cells (arrows) in endothelial cell lining of mother vessels that subsequently develop into GBs. d–g: Immunohistochemical staining demonstrates that primitive precursor cells (black arrows) bear endothelial cell markers (CD-31) (d), relatively increased staining for VEGFR-2 (e), but lack pericyte markers (α-SMA) (f). White arrow in f indicates α-SMA-positive pericytes just peripheral to primitive GBs (black arrow). Staining for basement membrane proteins, decreased or lost during the course of mother vessel formation, 1 is now increased in intensity (entactin) (g). m, mother vessels; lip, osmophilic, lipid-filled cell. Scale bars, 25 μm.
