Figure 4.
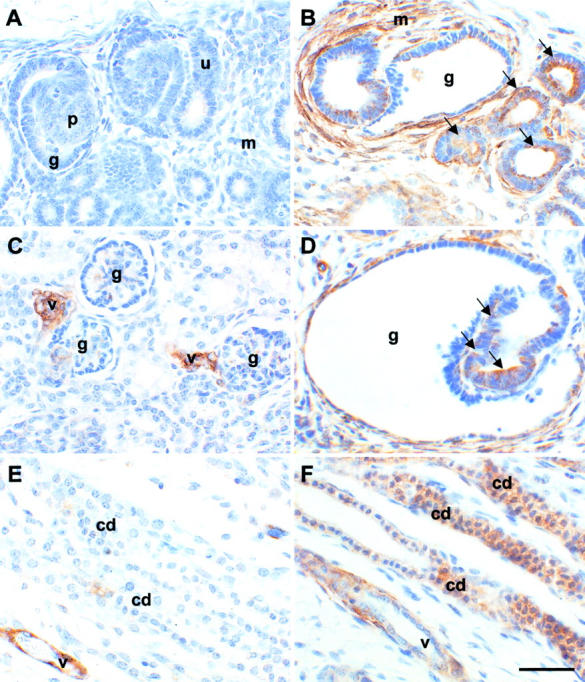
Localization of α-SMA protein in sham-operated and obstructed ovine fetal kidneys. All sections were stained with anti-α-SMA antibodies. A, C, and E are sections of sham-operated kidneys whereas B, D, and F are from obstructed kidneys. A and B show the outer cortex; C and D show areas deeper in the cortex; E and F show the medulla. No staining was observed in control experiments when the primary antibody was omitted (data not shown). A: Significant α-SMA immunoreactivity was not detected in ureteric bud tips (u), developing proximal tubules (p), or glomeruli (g), or in mesenchymal areas (m) in the outer cortex of sham-operated kidneys. B: Strong expression of this protein was detected, however, in the mesenchyme-like tissues (m) around dilated epithelia in obstructed kidneys, and in some tubule epithelia (arrows) and glomerular cysts (g). C: Deeper in the cortex, α-SMA was detected in normal glomeruli (g) and in vessels (v). D: There was, however, striking up-regulation of α-SMA around dilated glomeruli (g) and in aberrant glomerular tuft epithelia (arrows) in obstructed kidneys. E: In the normal medulla, minimal α-SMA immunoreactivity was detected in collecting ducts (cd), whereas vessels were strongly positive. F: In obstructed kidneys, up-regulated α-SMA expression was observed in dilated collecting ducts; staining intensity of these dilated ducts was comparable to the vessels. Scale bar, 15 μm.
