Figure 1.
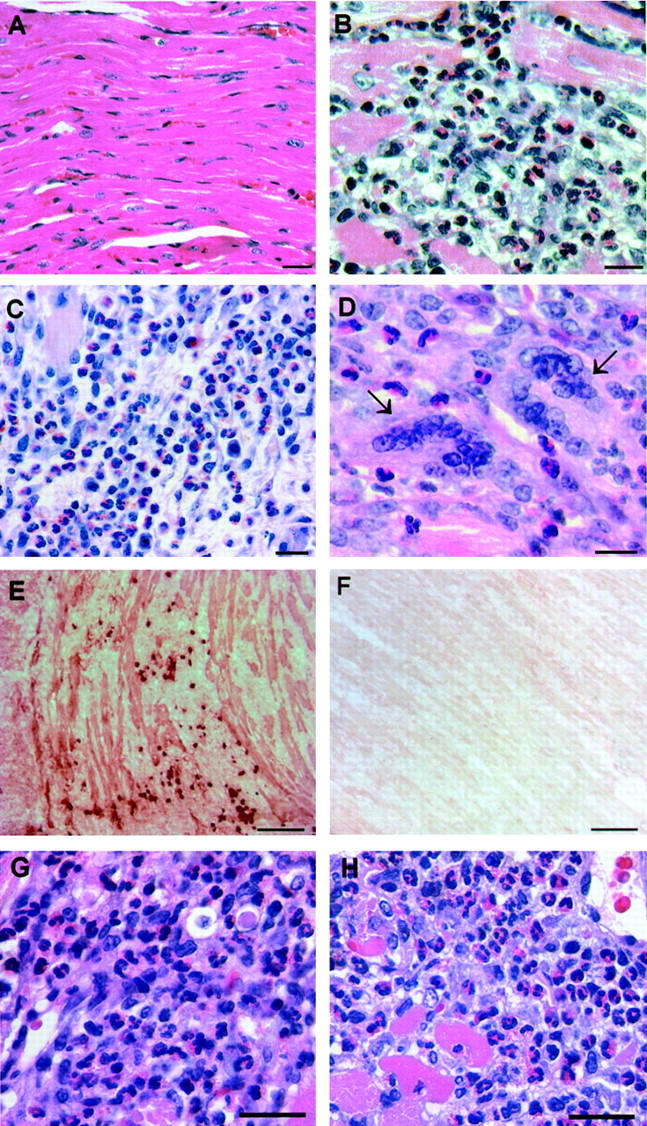
Th2-like characteristics of the heart infiltrate in EAM. A/J mice immunized with CM were sacrificed on day 21 and their hearts were removed for histological examination. A: Normal heart. B and C: Heart infiltrate in EAM is characterized by the presence of abundant eosinophils. D: Heart infiltrate contains giant cells (arrows); eosinophils are seen in the vicinity of giant cells. E: IgG1 deposition and IgG1-positive cells in EAM were detected by immunohistochemistry. The positive stain was visualized with 3-amino-9-ethyl-carbazole substrate solution. Shown heart has a grade 3 lesion. F: Background staining of the same heart using a rat IgG2a isotype control mAb. G and H: Eosinophils in heart lesions in a splenocyte transfer model of EAM. Donor mice were immunized with either CM (G) or with myhcα(334-352) peptide (H). Their splenocytes were collected on day 21 after immunization, stimulated in culture for 3 days with 10 μg/ml of either CM (G) or the peptide (H), and transferred into the recipient mice in a dose of 5 × 10 7 cells. Recipients were sacrificed on day 14 after transfer and their hearts were assessed for the presence of myocarditis. H&E stain (A–D, G, and H); Congo Red (C). Scale bars: 25 μm (A–D), 100 μm (E and F), and 20 μm (G and H).
