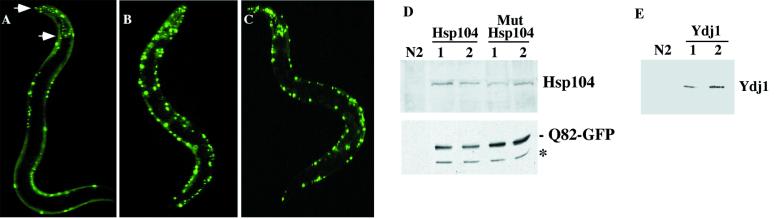
Figure 4.
Expression of wild-type Hsp104 diminishes aggregation of Q82-GFP. To assess the effects of chaperone expression on polyglutamine aggregates, wild-type or mutant Hsp104 or Ydj1 (dnaJ chaperone) was coexpressed with Q82-GFP in body wall muscle cells (unc-54 promoter), whereas only Q82-GFP was expressed in the pharyngeal cells (myo-2 promoter). (A) Overexpression of Hsp104 reduced Q82-GFP aggregates in body wall muscle cells but not in the pharyngeal cells (between the arrows). In animals expressing mutant Hsp104 (B) or Ydj1 (C), Q82 aggregates were unaffected. (D and E) Immunoblot analysis of extracts of wild-type N2 or chaperone-expressing animals for (D) two lines, each expressing Hsp104 and mutant Hsp104 by using anti-Hsp104 and anti-GFP Ab (asterisk corresponds to mobility of free GFP); and (E) Ydj-1 levels in N2 animals and two lines expressing Ydj1.