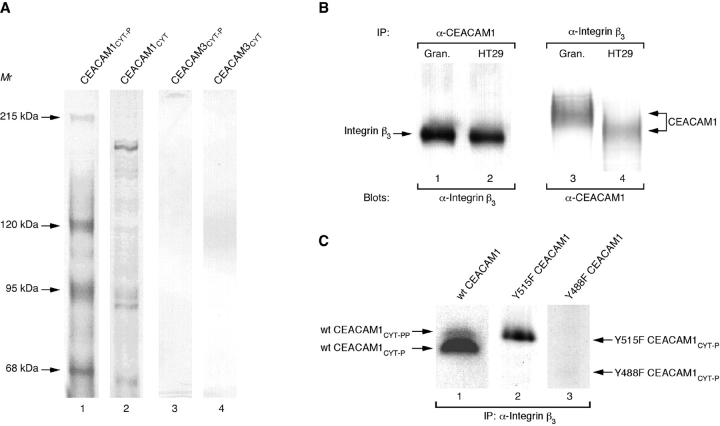
Figure 1.
Purification of CEACAM1cyt -associated proteins from granulocyte extracts. A: SDS-PAGE and silver staining of eluates from immobilized CEACAM domains. Extracts from granulocytes were subjected to purification on adjusted amounts of immobilized in vitro tyrosine phosphorylated CEACAM1cyt (lane 1), unphosphorylated CEACAM1cyt (lane 2), in vitro tyrosine phosphorylated CEACAM3cyt (lane 3), and unphosphorylated CEACAM3cyt (lane 4). Positions of the purified proteins mentioned in the text and apparent molecular masses are indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). B: Coprecipitation of integrin β3 and CEACAM1. Extracts from granulocytes (lanes 1 and 3) and HT29 cells (lanes 2 and 4) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with CEACAM1 mAb 12-140-4 (lanes 1 and 2) or anti-integrin β3 mAb (lanes 3 and 4). Bound proteins were resolved by 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotted with anti-integrin β3 mAb (lanes 1 and 2) or anti-CEACAM1 mAb 4D1/C2 (lanes 3 and 4). The positions of integrin β3 and CEACAM1 are indicated on the left or right. C: Coprecipitation of tyrosine phosphorylated wild-type and mutant CEACAM1cyt with anti-integrin β3 mAb. Following in vitro tyrosinephosphorylation, the radioactively labeled phosphoproteins (wild-type CEACAM1cyt (lane 1), Y515F CEACAM1cyt (lane 2), and Y488F CEACAM1cyt (lane 3)) and Protein G PLUS/Protein A-agarose were incubated with precleared granulocyte extracts containing integrin β3 mAb at 4°C for 2 hours. After immunoprecipitation, precipitates were resolved with 17.5% SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. Positions of labeled phosphoproteins areindicated on the left or right.