Figure 2.
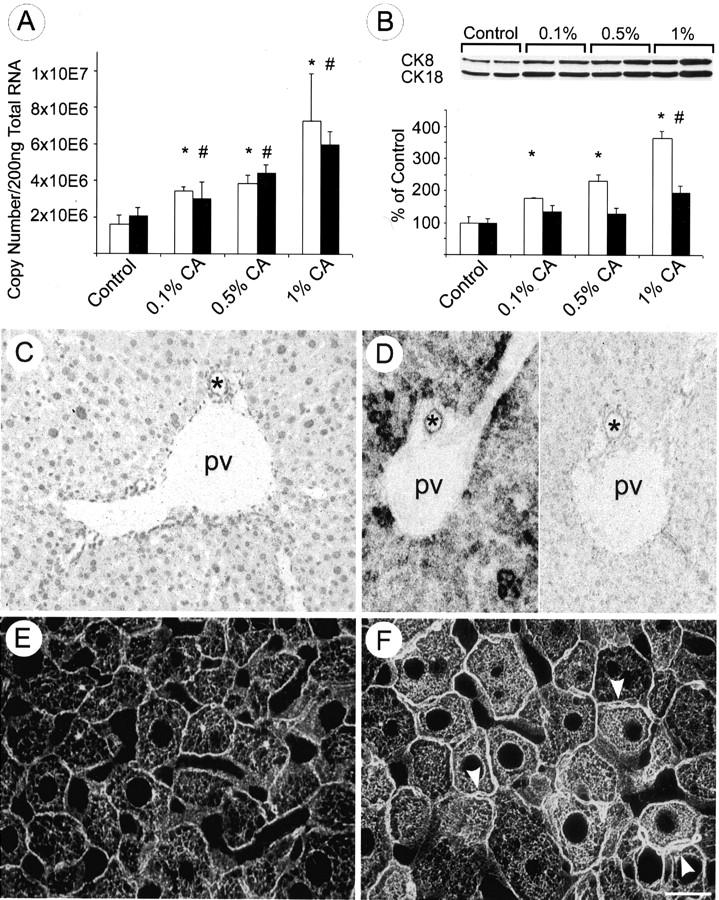
Effects of bile acid feeding on hepatic CK 8 and CK 18 expression and the intermediate filament cytoskeleton. A: Competitive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction revealed an increase of CK 8 (open bars) and CK 18 (black bars) mRNA after CA (0.1%, 0.5%, 1%) feeding for 7 days. Feeding a diet containing 1% CA led to an approximate threefold increase. Data (means + SEM) are expressed as copy numbers per 200 ng total RNA (n = 5 animals in each group; * and #, P < 0.05, CA-fed animals versus controls). B: CA feeding resulted in a dose-dependent increase of CK 8 protein (open bars) and CK 18 protein (black bars) levels. CK 8 protein levels increased twofold and 2.5-fold in 0.1 and 0.5% CA-fed animals, respectively, whereas CK 18 protein levels only slightly increased. However, 1% CA-fed mice showed 3.5-fold CK 8 and twofold CK18 elevation in comparison to controls. It is noteworthy that the increase of CK 8 clearly exceeded that of CK 18 (n = 5 animals in each group; * and #, P < 0.05, CA-fed animals versus controls). In situ hybridization for CK 8 mRNA in control liver (C) and in CA (1%, for 7 days)-fed mouse liver (D) (left side, anti-sense probe; right side, sense probe) showing that CA feeding resulted in a marked increase in CK 8 mRNA expression particularly in the periportal parenchyma. Immunofluorescence staining of IF cytoskeleton in normal liver (E) and increased density of the CK-IF network in CA-fed mouse liver particularly around the bile canaliculi (F, arrowheads; pv, portal vein; *, bile duct). Scale bar, 20 μm. Original magnifications, ×20 (C and D).
