Figure 4.
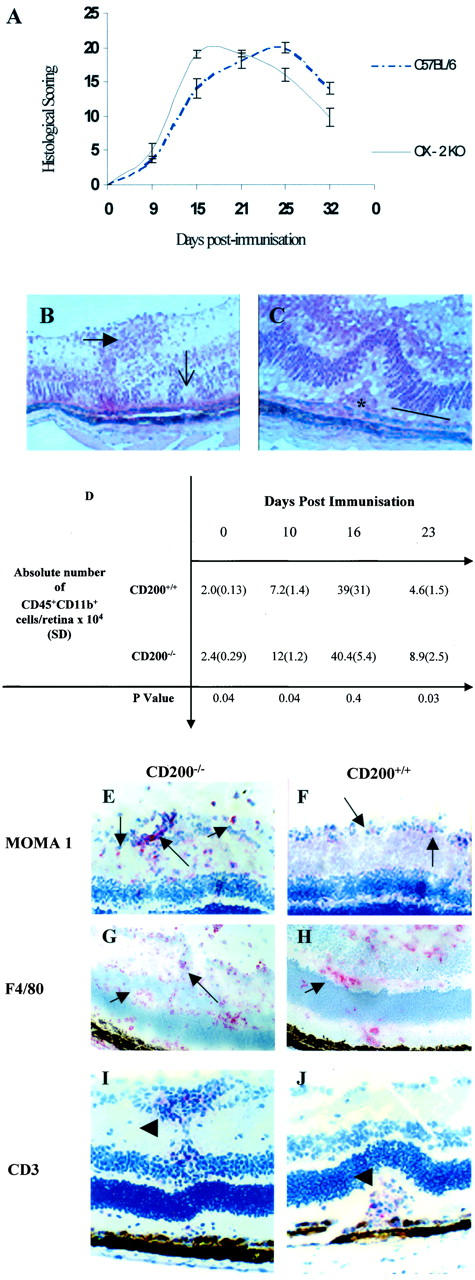
CD200−/− mice have an earlier and increased severity of IRBP peptide 1-20 induced EAU. A: Graphic representation of histological scoring of EAU disease severity in CD200−/− and CD200+/+mice, graded by combining infiltration levels in anterior and posterior areas with tissue damage. CD200−/− mice have an accelerated onset of disease achieving peak disease earlier than CD200+/+mice. Ultimately, the structural damage was not significantly different between the two groups. No difference in clinical disease features between CD200+/+ and CD200−/− mice were observed. B and C: Representative H&E preparations of retinal sections showing EAU features at day 16 after immunization and include retinal folds (open arrow), vasculitis (closed arrow), and photoreceptor cell destruction (line) and granuloma formation (asterisk). D: Absolute numbers of CD45+CD11b+ retinal infiltrate during EAU in CD200+/+ and CD200−/− mice, confirming earlier and increased inflammation in CD200−/− mice. MOMA-1 (E and F), F4/80 (G and H), and CD3 (I and J) were visualized with SA ABC-AP on section of retinal tissue from CD200−/− mice (E, G, and I) and CD200+/+ mice (F, H, and J). In CD200−/− mice, there is an increased infiltration of MOMA-1 and F4/80 cells (arrows) but CD3+ T cell infiltrate (arrowhead) is equivalent in both CD200−/− and CD200+/+ mice, as confirmed by flow cytometry (D). Original magnifications: ×300 (B); ×500 (C); ×200 (E, F, I, and J); ×150 (G and H).
