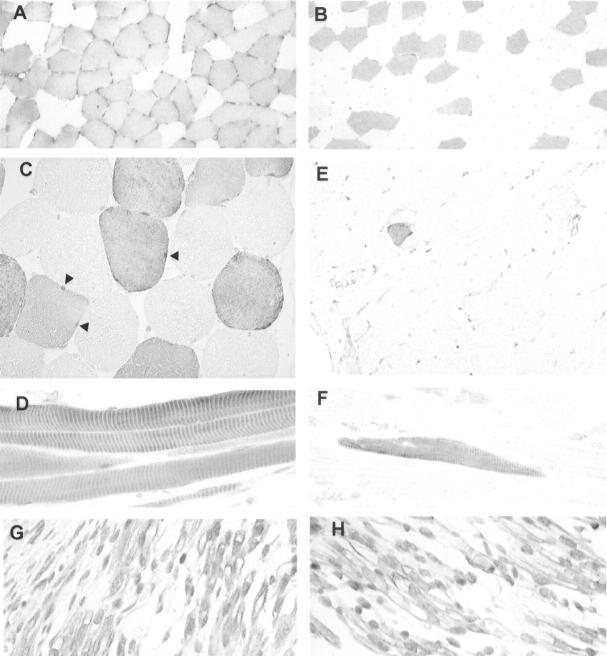
Figure 2.
Expression of Arpp and Carp in human skeletal muscle tissues demonstrated immunohistochemically. A: Cross-section of biceps femoris muscle immunostained with α-Arpp(FL) Ab. Arpp-positive myofibers are scattered randomly in a checkerboard-like pattern. B: Cross-section of quadriceps femoris muscle immunostained with α-Arpp(FL) Ab. C: Cross-section of skeletal muscle immunostained with α-Arpp(FL) Ab. Both nuclei (arrowheads) and cytoplasm of myofibers are positively stained. D: Longitudinal section of skeletal muscle immunostained with α-Arpp(FL) Ab. Positive immunoreactions coincide with muscle striation in Arpp-positive muscle fibers. E: Cross-section of skeletal muscle immunostained with α-Carp(N) Ab. Carp is undetectable in almost all myofibers. Very small numbers of Carp-positive myofibers were detected. F: Longitudinal section of skeletal muscle immunostained with α-Carp(N) Ab. Positive immunoreaction coincides with muscle striation in Carp-positive muscle fibers. G and H: Immunohistochemistry of skeletal muscle of fetus at 11 developmental weeks with α-Carp(N) Ab (G) and α-Arpp(FL) Ab (H). Both nuclei and cytoplasms are positively stained with α-Arpp(FL) Ab and α-Carp(N) Ab. Myocytes positively immunostained and those stained at only a trace level are observed (G, H). Original magnifications: ×100 (A, B, E); ×400 (C, D, F–H).