Figure 3.
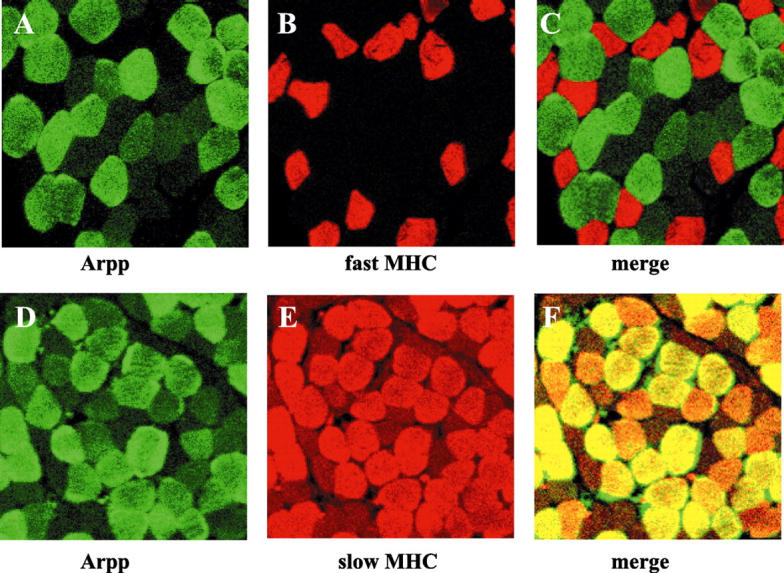
Muscle-type-specific expression of Arpp protein. Paraffin-embedded human skeletal muscle tissue sections were analyzed by double-immunostaining analysis using confocal microscopy. Skeletal muscle tissue sections were incubated with α-Arpp(FL) Ab and α-MHC(fast) Ab (A–C), or with α-Arpp(FL) Ab and α-MHC(slow) Ab (D–F). Subsequently, these first Abs were detected by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary Ab (green) or Alexa Fluor 546-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary Ab (red). Skeletal muscle fibers expressing Arpp (A and D, green), fast MHC (B, red) and slow MHC (E, red) were detected. When the signals reflecting the expression of Arpp and fast MHC or Arpp and slow MHC were merged (C and F), the resulting yellow signal indicated co-expression of Arpp and fast MHC or Arpp and slow MHC.
