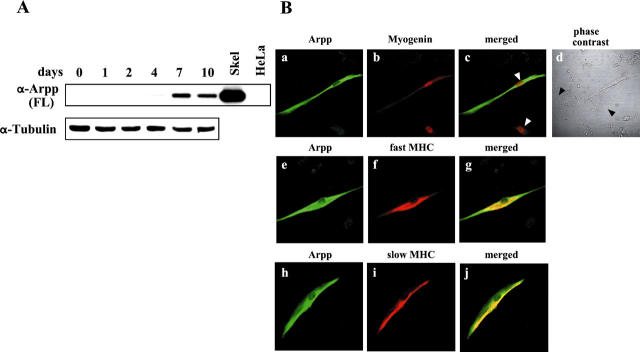
Figure 5.
Arpp is induced during differentiation of C2C12 cells. A: Western blot analysis of differentiating C2C12 cells for Arpp expression. After culture of C2C12 cells in DM for 0, 1, 2, 4, 7, or 10 days, the cells were collected and their lysates subjected to Western blotting using α-Arpp(FL) Ab. Mouse skeletal muscle (Skel) and HeLa cells (HeLa) were subjected to the same analysis as a positive and negative control, respectively. The same amount of the lysate was subjected to Western blotting using α-tubulin Ab as a loading control. B: Arpp is expressed in differentiated C2C12 cells. After culture for 7 days in DM, C2C12 cells were fixed and incubated with a mixture of α-Arpp(FL) Ab and α-myogenin Ab (a–c), α-MHC(fast) Ab (e–g), or α-MHC(slow) Ab (h–j). These first Abs were detected by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary Ab (green) or Alexa Fluor 546-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary Ab (red). Arpp was detected as green signals (a, e, h). Myogenin (b), fast MHC (f), and slow MHC (i) were detected as red signals. When both signals were merged, the resulting yellow signals reflect co-expression of Arpp and myogenin (c), Arpp and fast MHC (g), or Arpp and slow MHC (j). Myogenin was detected in the differentiated myocytes (red in b). Among the myogenin-expressing myotube-like cells, Arpp-positive myotube-like cells and Arpp undetectable myotube-like cells (white arrowheads in c) were admixed. After culture of C2C12 cells for 7 days in DM, among undifferentiated myoblast-like cells (black arrowheads in d), differentiated myotube-like cells were distributed.