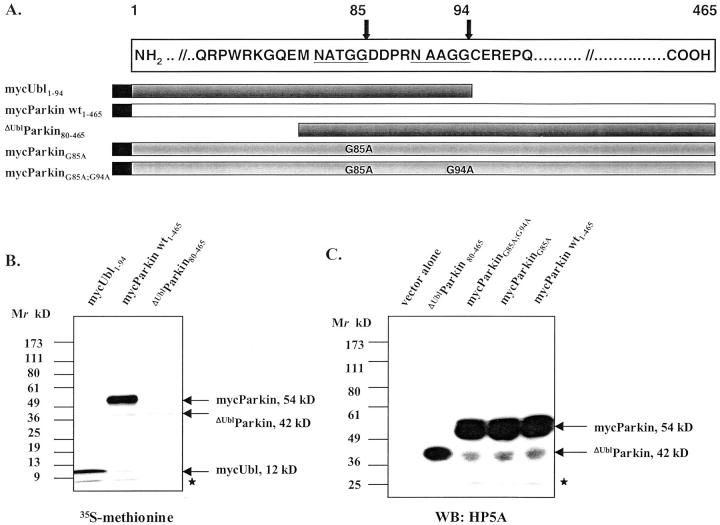
Figure 7.
Mutational analysis of parkin’s cleavage in HEK293 cells. A: Diagram of two –NAxGG- motifs (underlined) in the sequence of human parkin (numbering according to Kitada et al 3 ), and of cDNA constructs encoding parkin proteins, as indicated. B: PAGE and autoradiogram of in vitro-translated cDNA constructs encoding full-length and truncated parkin proteins. C: PAGE and Western blotting (WB) of HEK293 cell lysates transfected with cDNA constructs encoding wild-type and mutant parkin proteins, as indicated. Note, generation of the 42-kd C-terminal parkin fragment was not abolished in parkin mutants, as detected by anti-parkin HP5A. Identical results were obtained using anti-parkin HP2A. Asterisks in B and C denote nonspecific background bands.