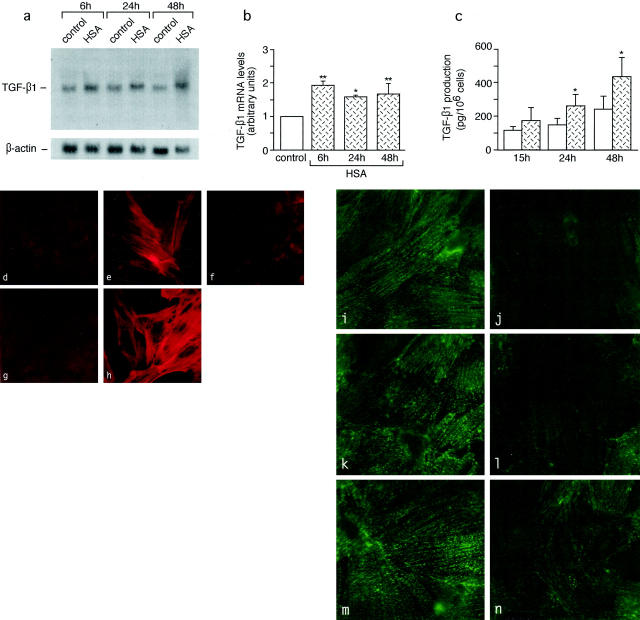
Figure 10.
Synthesis of TGF-β1, induction of downstream phenotypic change of mesangial cells, and loss of synaptopodin by podocytes in response to protein load. a–c: Effects of HSA on TGF-β1 mRNA expression by Northern blot analysis (a and b) and on TGF-β1 production by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (c) in cultured podocytes. *, P < 0.05 and **, P < 0.01 versus control. d–h: Expression of α-SMA in mesangial cells exposed to conditioned medium of unstimulated podocytes (d) or of HSA-stimulated podocytes alone (e) or in the presence of anti-TGF-β1 antibody (f), as assessed by fluorescence confocal microscopy. g and h: α-SMA in control mesangial cells either unstimulated (g) or exposed to TGF-β1 (h). i–n: Confocal microscopy analysis of the effect of HSA on podocyte synaptopodin. Podocytes exhibit marked reduction of synaptopodin staining after exposure to HSA for 6 hours (i) and 24 hours (l), and partial recovery at 48 hours (n) as compared to unstimulated control at the corresponding time points (i, k, and m). Original magnifications, ×1500.