Figure 5.
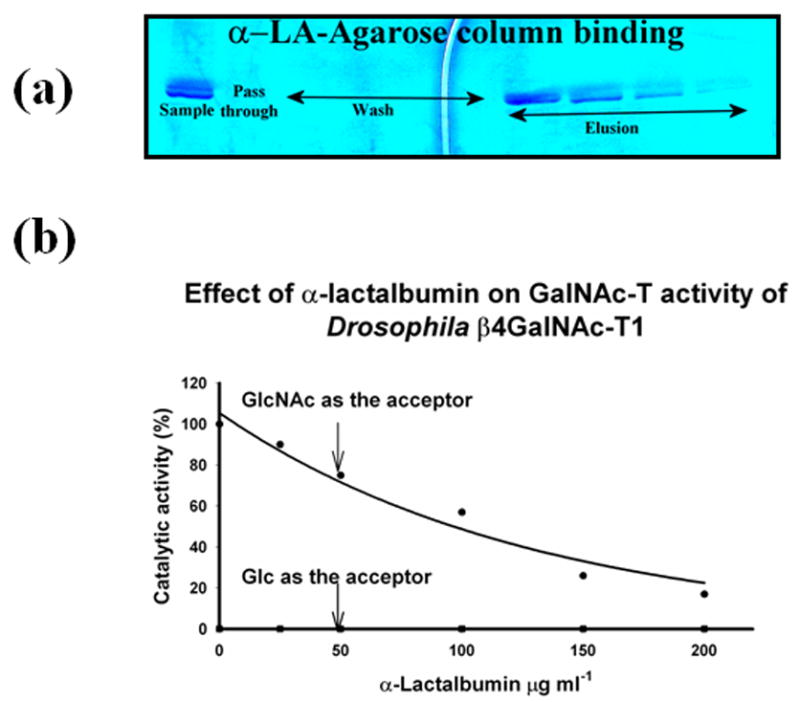
The binding of the in vitro folded recombinant Drosophila CG8536 protein to the α-LA-agarose column and inhibition of the protein’s GalNAc-T activity by α-LA. As shown by the SDS gel analysis (a), the in vitro folded protein also bound to the α-LA-agarose column in the presence of 10 mM GlcNAc and was eluted from the column with the buffer without GlcNAc. This property indicates that Drosophila CG8536 protein has an α-LA-binding site that can be accessed only in the presence of its substrate, a characteristic of mammalian β4Gal-T1.8, 16, 17 α-LA is known to bind mammalian β4Gal-T1 at the extended sugar-binding site,16 where it inhibits the transfer of galactose from UDP-Gal to GlcNAc or to an oligosaccharide. At the same time, α-LA enhances the transfer of galactose to glucose to make lactose. In the presence of recombinant bovine α-lactalbumin, the Drosophila CG8536 protein also inhibited the transfer of GalNAc from UDP-GalNAc to GlcNAc (b), or to chitobiose; however, it failed to transfer GalNAc to glucose (b). The 100% GalNAc-T activity corresponds to a specific activity of 32 pmol/min/μg of protein. GlcNAc and Glc concentrations were 25 mM each.
