Fig. 4.
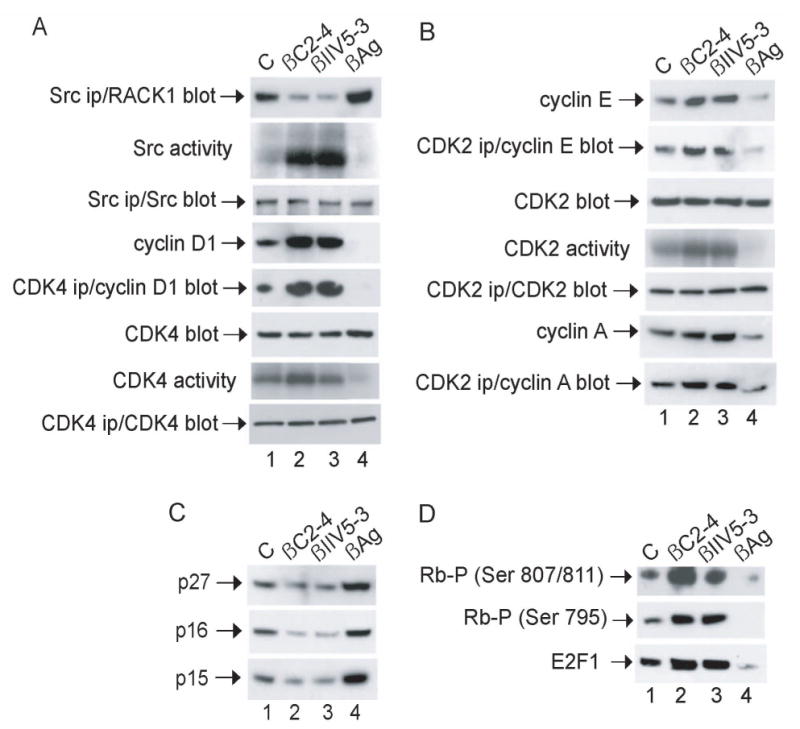
Effect of peptides on key regulators of G1/S transition in NIH 3T3 cells. Cells were synchronized in G0, released into G1 and incubated with peptide as described in the legend to Fig 3. (A and B) Proteins were precipitated with anti-Src, CDK4 or CDK2 from lysates containing 500 μg of cellular protein and analyzed for in vitro protein-kinase activity by incubating with [γ-32P]ATP together with MnCl2 and enolase (Src ips), MgCl2 and Rb peptide (CDK4 ips) or MgCl2 and histone H1 (CDK2 ips) for 10 min at 30°C, or subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-Src, CDK4 or CDK2, respectively. Otherwise, proteins from lysates containing 20 μg of cellular protein were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-CDK4, CDK2 or cyclin D1, E or A, as indicated. (C and D) Proteins from lysates containing 20 μg of cellular protein were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-p16, p15, p27, phospho-Rb (Ser 795 or Ser 807/811) or E2F1, as indicated. Data are representative of 2–3 independent experiments.
