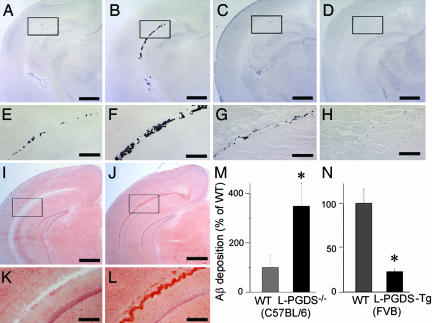
Fig. 5.
Inhibition of Aβ deposition by L-PGDS/β-trace in vivo. (A–H) Aβ deposition in the brain of WT mice (C57BL/6; A and E), L-PGDS−/− mice (C57BL/6; B and F), WT mice (FVB; C and G), and L-PGDS-Tg mice (FVB; D and H). (Scale bars: A–D, 1 mm; E–H, 200 μm.) (I–L) Congo-red staining of Aβ deposition in WT (C57BL/6; I and K) and L-PGDS−/− mice (C57BL/6; J and L) brain as described above. (Scale bar: I and J, 1 mm; K and L, 200 μm.) (M and N) The Aβ deposition was quantified by binding of [125I]-streptavidin to tissue sections prepared from the brain of WT and L-PGDS−/− mice (C57BL/6; M) and of WT and L-PGDS-Tg mice (FVB; N), which sections had been reacted with biotin-labeled Aβ (1–42). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3–4). Significant difference was based on Student's t test; ∗, P < 0.05.