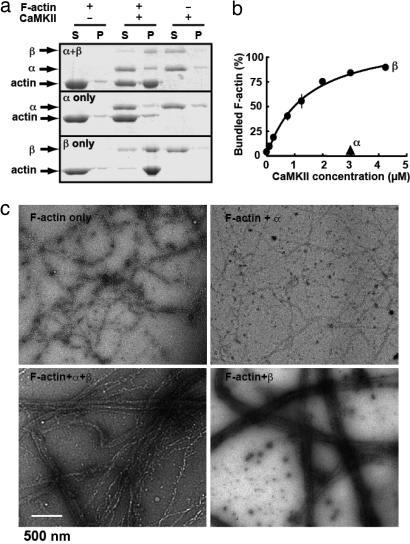
Fig. 1.
CaMKII bundles F-actin. (a) Cosedimentation of purified CaMKII and F-actin. F-actin formed in vitro was allowed to react with purified CaMKIIα/β, -α, or -β (all at 3 μM as monomer) for 30 min and sedimented at 10,000 × g for 10 min. Under this condition, the linear, unbundled F-actin stays in supernatant but bundled F-actin sediments. Both supernatant (S) and pellet (P) were separated on SDS/PAGE and stained with CBB. (b) Dose-dependent bundling of F-actin by CaMKIIβ. F-actin (3 μM as monomer) was incubated with increasing concentrations of CaMKIIβ (0.1–4.25 μM as monomer) and actin-bundling assays were performed. The amount of bundled F-actin was plotted against the concentration of CaMKIIβ. Mean± SEM. from three independent experiments is shown. (c) Negatively stained electron micrographs of F-actin in the presence or absence of purified CaMKII, all at 3 μM as monomer.