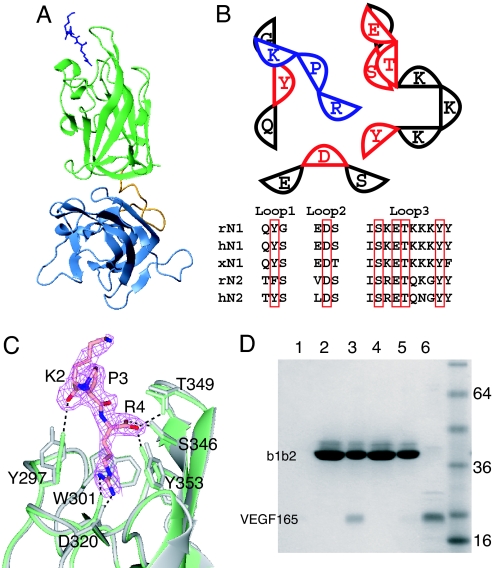
Fig. 2.
Location of the VEGF binding site on N1b1b2. (A) Ribbon diagram of N1b1b2/Tuftsin complex with N1b1b2 colored as in Fig. 1A and Tuftsin shown as blue sticks. (B) Schematic of the interaction between N1b1b2 (red and black) and Tuftsin (blue). The three ligand binding loops form the ligand binding surface on Nrp. The residues directly contacting Tuftsin (red) are conserved in Nrp-1 and Nrp-2, as shown in the sequence alignment among rat, human, and Xenopus Nrps (r, h, and x, respectively). (C) Atomic detail of the interaction between N1b1b2 (green) and Tuftsin shown with the 2Fo − Fc electron density map (pink) contoured at 0.9 σ. Hydrogen bonds between Tuftsin and N1b1b2 are indicated, and the structure of N1b1b2 in the absence of Tuftsin is shown in gray. (D) Mutation of Tuftsin-interacting residues in N1b1b2 (S346A, E348A, T349A) knocks out the ability of His-tagged N1b1b2 to pull down VEGF165 by using an immobilized metal affinity column. Shown are VEGF binding to resin alone (lane 1), wild-type N1b1b2 load (lane 2), wild-type N1b1b2 elute (lane 3), mutant N1b1b2 load (lane 4), mutant N1b1b2 elute (lane 5), and 50% VEGF165 load (lane 6).