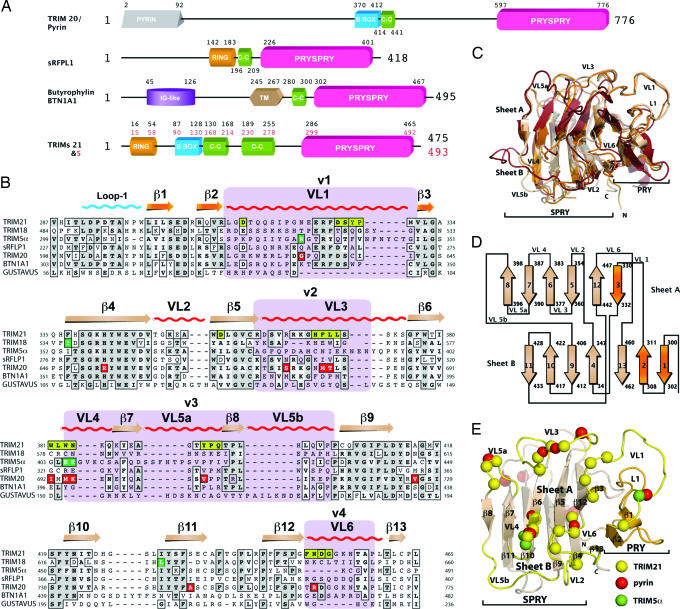
Fig. 1.
The PRYSPRY domain has a conserved binding interface that dictates function in TRIM and other protein families. (A) Domain architecture of TRIM proteins 20, 21, and 5α, Butyrophylin BTN1A1, and putative protein sRFPL1. Domain boundaries as predicted by SMART are indicated (47). (B) Sequence alignment of TRIM21 PRYSPRY with those of disease-related TRIM proteins and homologous SPRY domains. TRIM21 secondary structure elements are indicated along with the position of the canonical binding loops (VLs). TRIM21:Fc contact residues are shown in yellow boxes. Dark green boxes indicate the position of mutations in TRIM5α. Red boxes indicate pyrin mutations that confer FMF susceptibility. The four variable regions known to dictate viral restriction specificity in TRIM5α are marked in purple. Gray shading indicates sequence similarity. (C) Superposition of TRIM21 (wheat), GUSTAVUS (red), and sRFPL1 (orange). (D) PRYSPRY topology cartoon. The PRY subdomain is colored in orange and the SPRY is colored in wheat. (E) TRIM21 PRYSPRY binding site. Variable binding loops are indicated in yellow. Yellow spheres correspond to important contacts with Fc, green indicates TRIM5α mutations, and red shows pyrin mutations linked to FMF.