Figure 1.
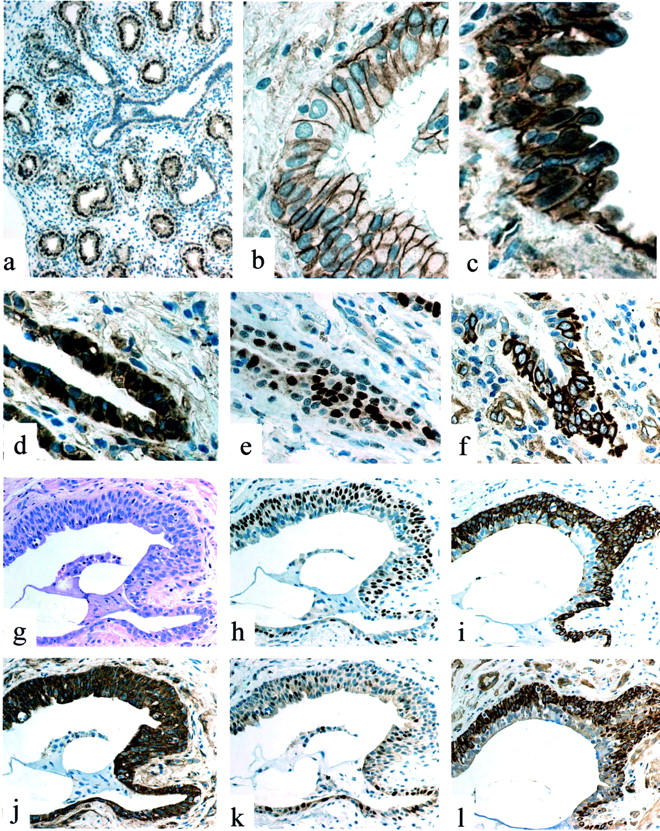
a: Fetal lung (12 weeks): nuclear expression of β-catenin is evident in alveolar buds, but not in airway cells. b: Normal lung: discrete membrane immunoreactivity of β-catenin in basal and ciliated cells in a bronchiole. c: IPF/UIP: aberrant nuclear accumulation of β-catenin in a proliferative bronchiolar lesion. d: IPF/UIP: nuclear expression of β-catenin in basal cells of an abnormal bronchiole. e: IPF/UIP (serial section to d): cyclin-D1-expressing cells. f: IPF/UIP (serial section to d): matrilysin/MMP-7 abnormal expression. g: IPF/UIP: H&E appearance of a small honeycombing bronchiolar lesion. h: IPF/UIP (serial section to g): basal cell hyperplasia as evidenced by ΔN-p63 nuclear expression. i: IPF/UIP (serial section to g): basal cell hyperplasia as evidenced by CK5 expression. j: IPF/UIP (serial section to g): abnormal intracellular expression of β-catenin in both basal and luminal epithelial cells. k: IPF/UIP (serial section to g): increased expression of cyclin-D1. l: IPF/UIP (serial section to g): aberrant expression of matrilysin/MMP-7 in basal cells.
